Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil?
Solution
N = 100,
R = 8 × 10−2 m,
I = 0.4 A,
μ0 = 4π × 10−7 T m/A
B = `(mu_0 "NI")/"2R"`
= `((4pi xx 10^-7)(100)(0.4))/(2(8 xx 10^-2))`
= 3.14 × 10−4 T
Hence, the magnitude of the magnetic field is 3.14 × 10−4 T.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
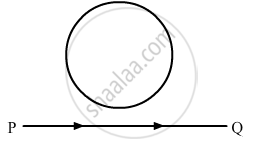
A conducting loop is held above a current carrying wire PQ as shown in the figure. Depict the direction of the current induced in the loop when the current in the wire PQ is constantly increasing.
A horizontal overhead power line carries a current of 90 A in east to west direction. What is the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field due to the current 1.5 m below the line?
Magnetic lines of force always cross each other
Explain the term hysteresis
Define magnetic lines of force
A particle of charge ‘q’ and mass ‘m’ is moving with velocity .`vecV` It is subjected to a uniform magnetic field `vecB` directed perpendicular to its velocity. Show that it describes a circular path. Write the expression for its radius.
A charged particle is moved along a magnetic field line. The magnetic force on the particle is
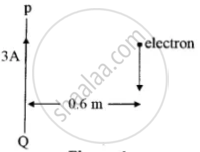
PQ is a long straight conductor carrying a current of 3A as shown in Figure below. An electron moves with a velocity of 2 x 107 ms-1 parallel to it. Find the force acting on the electron.
A charged particle is in motion having initial velocity `vecv` when it enters into a region of uniform magnetic field perpendicular to `vecv`. Because of the magnetic force the kinetic energy of the particle will ______.
According to the right-hand rule, the direction of magnetic induction if the current is directed in an anticlockwise direction is ______
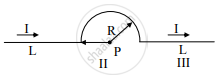
A conductor has three segments; two straights of length L and a semicircular with radius R. It carries a current I What is the magnetic field B at point P?
Show that currents in two long, straight, parallel wires exert forces on each other. Derive the expression for the force per unit length on each conductor.
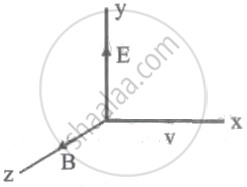
A particle with charge q moves with a velocity v in a direction perpendicular to the directions of uniform electric and magnetic fields, E and B respectively, which are mutually perpendicular to each other. Which one of the following gives the condition for which the particle moves undeflected in its original trajectory?
If a particle of charge 1012 coulomb moving along the `hat"x" -` direction with a velocity 102 m/s experiences a force of 1 o-s newton in `hat"y" -` direction due to magnetic field, then the minimum magnetic field is ____________.
A proton enters into a magnetic field of induction 1.732 T, with a velocity of 107 m/s at an angle 60° to the field. The force acting on the proton is e = 1.6 × 10-19 C, sin 60° = cos 30° = `sqrt3/2`
A solenoid 60 cm long and of radius 4.0 cm has 3 layers of windings of 300 turns each. A 2.0 cm long wire of mass 2.5 g lies inside the solenoid (near its centre) normal to its axis; both the wire and the axis of the solenoid are in the horizontal plane. The wire is connected through two leads parallel to the axis of the solenoid to an external battery which supplies a current of 6.0 A in the wire. What value of current (with appropriate sense of circulation) in the windings of the solenoid can support the weight of the wire? (g = 9.8 m s–2)
Direction of magnetic force on a positive charge moving in a magnetic field is given by ______.
Assertion: Free electrons always keep on moving in a conductor even then no magnetic force act on them in magnetic field unless a current is passed through it.
Reason: The average velocity of free electron is zero.
A deuteron of kinetic energy 50 keV is describing a circular orbit of radius 0.5 metre in a plane perpendicular to the magnetic field B. The kinetic energy of the proton that describes a circular orbit of radius 0.5 metre in the same plane with the same B is ______.
- perpendicular to direction of velocity of charged particle.
-
perpendicular to direction of magnetic field.
-
parallel to direction of velocity of charged particle.
-
parallel to the direction of magnetic field.
The magnetic moment of a current I carrying circular coil of radius r and number of turns N varies as ______.
Which one of the following is a correct statement about magnetic forces?
What is the magnetic induction of the field at the point O in a current I carrying wire that has the shape shown in the figure? The radius of the curved part of the wire is R, the linear parts are assumed to be very long.

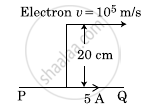
An infinitely long straight conductor carries a current of 5 A as shown. An electron is moving with a speed of 105 m/s parallel to the conductor. The perpendicular distance between the electron and the conductor is 20 cm at an instant. Calculate the magnitude of the force experienced by the electron at that instant.
A circular current loop of magnetic moment M is in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane is ______.
Consider a wire carrying a steady current, I placed in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to its length. Consider the charges inside the wire. It is known that magnetic forces do no work. This implies that ______.
- motion of charges inside the conductor is unaffected by B since they do not absorb energy.
- some charges inside the wire move to the surface as a result of B.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the force.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the magnetic force on the ions, assumed fixed within the wire.
A charged particle would continue to move with a constant velocity in a region wherein ______.
- E = 0, B ≠ 0.
- E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0.
- E ≠ 0, B = 0.
- E = 0, B = 0.
A charged particle of charge e and mass m is moving in an electric field E and magnetic field B. Construct dimensionless quantities and quantities of dimension [T]–1.
The unit Wbm-2 is equal to ______.
A charge particle moves along circular path in a uniform magnetic field in a cyclotron. The kinetic energy of the charge particle increases to 4 times its initial value. What will be the ratio of new radius to the original radius of circular path of the charge particle:
At a certain place the angle of dip is 30° and the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field is 0.5 G. The earth’s total magnetic field (in G), at that certain place, is ______.
Two conducting rails are connected to a source of emf and form an incline as shown in figure. A bar of mass 50 g slides without friction down the incline through a vertical magnetic field B. If the length of the bar is 50 cm and a current of 2.5 A is provided by battery. Value of B for which the bar slide at a constant velocity ______ × 10-1 Tesla. 2 [g = 10 m/s2]
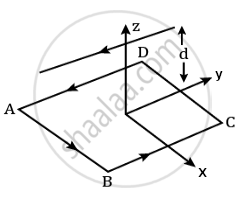
Figure shows a square loop. 20 cm on each side in the x-y plane with its centre at the origin. The loop carries a current of 7 A. Above it at y = 0, z = 12 cm is an infinitely long wire parallel to the x axis carrying a current of 10 A. The net force on the loop is ______ × 10-4 N.
A unit vector is represented as `(0.8hat"i" + "b"hat"j" + 0.4hat"k")`. Hence the value of 'b' must be ______.
Write the expression for the Lorentz force on a particle of charge q moving with a velocity `vecv` in a magnetic field `vecB`. When is the magnitude of this force maximum? Show that no work is done by this force on the particle during its motion from point `vecr_1` to point `vecr_2`.
An electron is moving along positive x-axis in a magnetic field which is parallel to the positive y-axis. In what direction will the magnetic force be acting on the electron?
With a neat labelled diagram, explain cyclotron motion and cyclotron formula.
Distinguish between the forces experienced by a moving charge in a uniform electric field and in a uniform magnetic field. (Any two points)
A circular coil of wire is made up of 200 turns, each of radius 10 cm. If a current of 0.5A passes through it, what will be the Magnetic field at the centre of the coil?
