Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A furniture dealer deals in tables and chairs. He has ₹ 1,50,000 to invest and a space to store at most 60 pieces. A table costs him ₹ 1500 and a chair ₹ 750. Construct the inequations and find the feasible solution.
Solution
Let x be the number of tables and y be the number of chairs. Then x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
The dealer has a space to store at most 60 pieces.
∴ x + y ≤ 60
Since, the cost of each table is ₹ 1500 and that of each chair is ₹ 750, the total cost of x tables and y chairs is 1500x + 750y. Since the dealer has ₹ 1,50,000 to invest, 1500x + 750y ≤ 1,50,000 = 2x + y ≤ 200
Hence the system of inequations are
x + y ≤ 60, 2x + y ≤ 200
First we draw the lines AB and CD whose equations are
x + y = 60 and 2x + y = 200, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 respectively.
| Line | Equation | Points on the X-axis | Points on the Y-axis | Sign | Region |
| AB | x + y = 60 | A(60,0) | B(0,60) | ≤ | origin side of line AB |
| CD | 2x + y = 200 | C(100,0) | D(0,200) | ≤ | origin side of line CD |
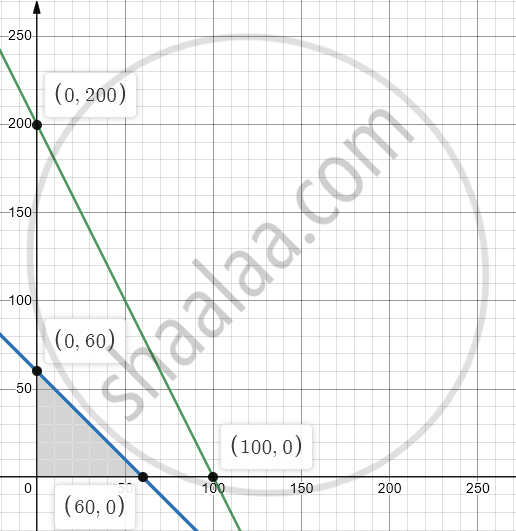
The feasible solution is shaded in the graph.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the feasible solution of the following inequation:
3x + 2y ≤ 18, 2x + y ≤ 10, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Find the feasible solution of the following inequation:
3x + 4y ≥ 12, 4x + 7y ≤ 28, y ≥ 1, x ≥ 0.
A company manufactures two types of chemicals Aand B. Each chemical requires two types of raw material P and Q. The table below shows number of units of P and Q required to manufacture one unit of A and one unit of B and the total availability of P and Q.
| Chemical→ | A | B | Availability |
| Raw Material ↓ | |||
| P | 3 | 2 | 120 |
| Q | 2 | 5 | 160 |
The company gets profits of ₹ 350 and ₹ 400 by selling one unit of A and one unit of B respectively. (Assume that the entire production of A and B can be sold). How many units of the chemicals A and B should be manufactured so that the company gets a maximum profit? Formulate the problem as LPP to maximize profit.
A company manufactures two types of fertilizers F1 and F2. Each type of fertilizer requires two raw materials A and B. The number of units of A and B required to manufacture one unit of fertilizer F1 and F2 and availability of the raw materials A and B per day are given in the table below:
| Fertilizers→ | F1 | F2 | Availability |
| Raw Material ↓ | |||
| A | 2 | 3 | 40 |
| B | 1 | 4 | 70 |
By selling one unit of F1 and one unit of F2, the company gets a profit of ₹ 500 and ₹ 750 respectively. Formulate the problem as LPP to maximize the profit.
A doctor has prescribed two different units of foods A and B to form a weekly diet for a sick person. The minimum requirements of fats, carbohydrates and proteins are 18, 28, 14 units respectively. One unit of food A has 4 units of fat, 14 units of carbohydrates and 8 units of protein. One unit of food B has 6 units of fat, 12 units of carbohydrates and 8 units of protein. The price of food A is ₹ 4.5 per unit and that of food B is ₹ 3.5 per unit. Form the LPP, so that the sick person’s diet meets the requirements at a minimum cost.
The company makes concrete bricks made up of cement and sand. The weight of a concrete brick has to be at least 5 kg. Cement costs ₹ 20 per kg and sand costs of ₹ 6 per kg. Strength consideration dictates that a concrete brick should contain minimum 4 kg of cement and not more than 2 kg of sand. Form the L.P.P. for the cost to be minimum.
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Maximize z = 7x + 11y, subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 26, 5x + 3y ≤ 30, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Minimize z = 8x + 10y, subject to 2x + y ≥ 7, 2x + 3y ≥ 15, y ≥ 2, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
The corner points of the feasible solution are (0, 0), (2, 0), `(12/7, 3/7)`, (0, 1). Then z = 7x + y is maximum at ______.
If the corner points of the feasible solution are (0, 10), (2, 2) and (4, 0), then the point of minimum z = 3x + 2y is ______.
Solve the following LPP:
Maximize z = 4x + 2y subject to 3x + y ≤ 27, x + y ≤ 21, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following LPP:
Maximize z = 6x + 10y subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 10, 5x + 3y ≤ 15, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve each of the following inequations graphically using XY-plane:
5y - 12 ≥ 0
A carpenter makes chairs and tables. Profits are ₹ 140 per chair and ₹ 210 per table. Both products are processed on three machines: Assembling, Finishing and Polishing. The time required for each product in hours and availability of each machine is given by the following table:
| Product → | Chair (x) | Table (y) | Available time (hours) |
| Machine ↓ | |||
| Assembling | 3 | 3 | 36 |
| Finishing | 5 | 2 | 50 |
| Polishing | 2 | 6 | 60 |
Formulate the above problem as LPP. Solve it graphically
A firm manufactures two products A and B on which profit earned per unit ₹ 3 and ₹ 4 respectively. Each product is processed on two machines M1 and M2. The product A requires one minute of processing time on M1 and two minutes of processing time on M2, B requires one minute of processing time on M1 and one minute of processing time on M2. Machine M1 is available for use for 450 minutes while M2 is available for 600 minutes during any working day. Find the number of units of product A and B to be manufactured to get the maximum profit.
A firm manufacturing two types of electrical items A and B, can make a profit of ₹ 20 per unit of A and ₹ 30 per unit of B. Both A and B make use of two essential components a motor and a transformer. Each unit of A requires 3 motors and 2 transformers and each units of B requires 2 motors and 4 transformers. The total supply of components per month is restricted to 210 motors and 300 transformers. How many units of A and B should be manufactured per month to maximize profit? How much is the maximum profit?
A company manufactures two types of chemicals A and B. Each chemical requires two types of raw material P and Q. The table below shows number of units of P and Q required to manufacture one unit of A and one unit of B.
| Raw Material \Chemical | A | B | Availability |
| p | 3 | 2 | 120 |
| Q | 2 | 5 | 160 |
The company gets profits of ₹ 350 and ₹ 400 by selling one unit of A and one unit of B respectively. Formulate the problem as L.P.P. to maximize the profit.
Solve the following L.P.P. by graphical method:
Maximize: Z = 4x + 6y
Subject to 3x + 2y ≤ 12, x + y ≥ 4, x, y ≥ 0.
Choose the correct alternative :
Which of the following is correct?
Objective function of LPP is ______.
Choose the correct alternative :
Solution of LPP to minimize z = 2x + 3y st. x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 1≤ x + 2y ≤ 10 is
Fill in the blank :
“A gorage employs eight men to work in its shownroom and repair shop. The constraints that there must be at least 3 men in showroom and at least 2 men in repair shop are ______ and _______ respectively.
State whether the following is True or False :
The point (1, 2) is not a vertex of the feasible region bounded by 2x + 3y ≤ 6, 5x + 3y ≤ 15, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
State whether the following is True or False :
The feasible solution of LPP belongs to only quadrant I.
Minimize z = 2x + 4y is subjected to 2x + y ≥ 3, x + 2y ≥ 6, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 show that the minimum value of z occurs at more than two points
x − y ≤ 1, x − y ≥ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 are the constant for the objective function z = x + y. It is solvable for finding optimum value of z? Justify?
State whether the following statement is True or False:
Objective function of LPP is a relation between the decision variables
State whether the following statement is True or False:
LPP is related to efficient use of limited resources
Solve the following linear programming problems by graphical method.
Maximize Z = 40x1 + 50x2 subject to constraints 3x1 + x2 ≤ 9; x1 + 2x2 ≤ 8 and x1, x2 ≥ 0.
Solve the following linear programming problems by graphical method.
Minimize Z = 20x1 + 40x2 subject to the constraints 36x1 + 6x2 ≥ 108; 3x1 + 12x2 ≥ 36; 20x1 + 10x2 ≥ 100 and x1, x2 ≥ 0.
In the given graph the coordinates of M1 are

Which of the following can be considered as the objective function of a linear programming problem?
The optimal value of the objective function is attained at the ______ of feasible region.
For the following shaded region, the linear constraint are:
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Maximize: z = 3x + 5y Subject to: x + 4y ≤ 24, 3x + y ≤ 21, x + y ≤ 9, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Sketch the graph of the following inequation in XOY co-ordinate system.
x + y ≤ 0
Sketch the graph of the following inequation in XOY co-ordinate system.
2y - 5x ≥ 0
