Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A random variable X takes the values 0, 1, 2 and 3 such that:
P (X = 0) = P (X > 0) = P (X < 0); P (X = −3) = P (X = −2) = P (X = −1); P (X = 1) = P (X = 2) = P (X = 3) . Obtain the probability distribution of X.
Solution
Let P (X = 0) = k. Then,
P (X = 0) = P (X > 0) = P (X < 0)
P (X < 0) = k ∴ P (X = 0) + P (X > 0) + P (X < 0) = 1
\[\Rightarrow k + k + k = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow k = \frac{1}{3}\]
Now,
P (X < 0) = k
\[ \Rightarrow 3P\left( X = - 1 \right) = k ................ \left [ \because P\left( X = - 1 \right) = P\left( X = - 2 \right) = P\left( X = - 3 \right) \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow P\left( X = - 1 \right) = \frac{k}{3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow P\left( X = - 1 \right) = \frac{1}{3} \times \frac{1}{3} = \frac{1}{9}\]
\[ \therefore P\left( X = - 1 \right) = P\left( X = - 2 \right) = P\left( X = - 3 \right) = \frac{1}{9}\]
\[\text{ Similarly,} \]
\[P\left( X > 0 \right) = k\]
\[ \Rightarrow P\left( X = 1 \right) = P\left( X = 2 \right) = P\left( X = 3 \right) = \frac{1}{9}\]
| Xi | Pi |
| -3 |
\[\frac{1}{9}\]
|
| -2 |
\[\frac{1}{9}\]
|
| -1 |
\[\frac{1}{9}\]
|
| 1 |
\[\frac{1}{9}\]
|
| 2 |
\[\frac{1}{9}\]
|
| 3 |
\[\frac{1}{9}\]
|
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
then E(X)=....................
Assume that the chances of the patient having a heart attack are 40%. It is also assumed that a meditation and yoga course reduce the risk of heart attack by 30% and prescription of certain drug reduces its chances by 25%. At a time a patient can choose any one of the two options with equal probabilities. It is given that after going through one of the two options the patient selected at random suffers a heart attack. Find the probability that the patient followed a course of meditation and yoga?
A random variable X ~ N (0, 1). Find P(X > 0) and P(X < 0).
Two numbers are selected at random (without replacement) from the first five positive integers. Let X denote the larger of the two numbers obtained. Find the mean and variance of X
There are 4 cards numbered 1 to 4, one number on one card. Two cards are drawn at random without replacement. Let X denote the sum of the numbers on the two drawn cards. Find the mean and variance of X.
Let, X denote the number of colleges where you will apply after your results and P(X = x) denotes your probability of getting admission in x number of colleges. It is given that
where k is a positive constant. Find the value of k. Also find the probability that you will get admission in (i) exactly one college (ii) at most 2 colleges (iii) at least 2 colleges.
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| Values of X : | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X) : | 0.1 | k | 0.2 | 2k | 0.3 | k |
Find the value of k.
The probability distribution function of a random variable X is given by
| xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| pi : | 3c3 | 4c − 10c2 | 5c-1 |
where c > 0 Find: P (X < 2)
An urn contains 4 red and 3 blue balls. Find the probability distribution of the number of blue balls in a random draw of 3 balls with replacement.
From a lot of 10 bulbs, which includes 3 defectives, a sample of 2 bulbs is drawn at random. Find the probability distribution of the number of defective bulbs.
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k |
\[\frac{k}{2}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{8}\]
|
Find P(X ≤ 2) + P(X > 2) .
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| pi : | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | -3 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| pi : | 0.05 | 0.45 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.05 |
A fair coin is tossed four times. Let X denote the longest string of heads occurring. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
A die is tossed twice. A 'success' is getting an odd number on a toss. Find the variance of the number of successes.
A box contains 13 bulbs, out of which 5 are defective. 3 bulbs are randomly drawn, one by one without replacement, from the box. Find the probability distribution of the number of defective bulbs.
Write the values of 'a' for which the following distribution of probabilities becomes a probability distribution:
| X= xi: | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| P(X= xi) : |
\[\frac{1 - a}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{1 + 2a}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{1 - 2a}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{1 + a}{4}\]
|
If X is a random-variable with probability distribution as given below:
| X = xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X = xi) : | k | 3 k | 3 k | k |
The value of k and its variance are
Five bad oranges are accidently mixed with 20 good ones. If four oranges are drawn one by one successively with replacement, then find the probability distribution of number of bad oranges drawn. Hence find the mean and variance of the distribution.
For the following probability density function (p. d. f) of X, find P(X < 1) and P(|x| < 1)
`f(x) = x^2/18, -3 < x < 3`
= 0, otherwise
If the demand function is D = 150 - p2 - 3p, find marginal revenue, average revenue and elasticity of demand for price p = 3.
John and Mathew started a business with their capitals in the ratio 8 : 5. After 8 months, john added 25% of his earlier capital as further investment. At the same time, Mathew withdrew 20% of bis earlier capital. At the end of the year, they earned ₹ 52000 as profit. How should they divide the profit between them?
The expenditure Ec of a person with income I is given by Ec = (0.000035) I2 + (0. 045) I. Find marginal propensity to consume (MPC) and average propensity to consume (APC) when I = 5000.
If X ∼ N (4,25), then find P(x ≤ 4)
Solve the following :
Identify the random variable as either discrete or continuous in each of the following. Write down the range of it.
20 white rats are available for an experiment. Twelve rats are male. Scientist randomly selects 5 rats number of female rats selected on a specific day
Solve the following:
Identify the random variable as either discrete or continuous in each of the following. Write down the range of it.
A highway safety group is interested in studying the speed (km/hrs) of a car at a check point.
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(x) | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | –0.1 | 0.3 |
The probability that a bulb produced by a factory will fuse after 200 days of use is 0.2. Let X denote the number of bulbs (out of 5) that fuse after 200 days of use. Find the probability of X ≤ 1
Let the p.m.f. of a random variable X be P(x) = `(3 - x)/10`, for x = −1, 0, 1, 2 = 0, otherwise Then E(x) is ______
Find the probability distribution of the number of doublets in three throws of a pair of dice
Let X be a discrete random variable. The probability distribution of X is given below:
| X | 30 | 10 | – 10 |
| P(X) | `1/5` | `3/10` | `1/2` |
Then E(X) is equal to ______.
A discrete random variable X has the probability distribution given as below:
| X | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| P(X) | k | k2 | 2k2 | k |
Find the value of k
The random variable X can take only the values 0, 1, 2. Given that P(X = 0) = P(X = 1) = p and that E(X2) = E[X], find the value of p
Let X be a discrete random variable whose probability distribution is defined as follows:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"(x + 1), "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3"," 4),(2"k"x, "for" x = 5"," 6"," 7),(0, "Otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate the value of k
The probability distribution of a discrete random variable X is given as under:
| X | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2A | 3A | 5A |
| P(X) | `1/2` | `1/5` | `3/25` | `1/10` | `1/25` | `1/25` |
Calculate: Variance of X
Box I contains 30 cards numbered 1 to 30 and Box II contains 20 cards numbered 31 to 50. A box is selected at random and a card is drawn from it. The number on the card is found to be a nonprime number. The probability that the card was drawn from Box I is ______.
Kiran plays a game of throwing a fair die 3 times but to quit as and when she gets a six. Kiran gets +1 point for a six and –1 for any other number.
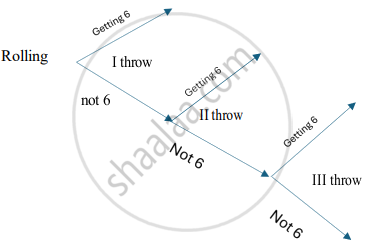
- If X denotes the random variable “points earned” then what are the possible values X can take?
- Find the probability distribution of this random variable X.
- Find the expected value of the points she gets.
