Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following
Explain the ammonolysis of alkyl halides.
Solution
i. When alkyl halide is heated with an alcoholic solution of excess ammonia, it undergoes a nucleophilic substitution reaction in which the halogen atom is replaced by an amino (–NH2) group to form primary amine.
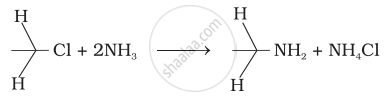
ii. This process of breaking of the C – X bond by ammonia is known as ammonolysis. The reaction is also known as the alkylation of ammonia. The reaction is carried out in a sealed tube at 373 K.
iii. The primary amine obtained in the1st step is stronger nucleophile than ammonia. Hence, it further reacts with an alkyl halide to form secondary and tertiary amines and finally quaternary ammonium salt if NH3 is not used in large excess.
\[\ce{\underset{\text{Alkyl halide}}{R - X} + \underset{\text{(excess)}}{NH3_{(alc.)}}->[\Delta] \underset{1^0}{R} - NH2 + HX}\]
iv. The order of reactivity of alkyl halides with ammonia is R–I > R–Br > R–Cl.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are propan-1-amine and propan-2-amine prepared from oxime?
Write a short note on Hoffmann bromamide degradation.
Identify the compounds 'A' and 'B' in the following equation:

Accomplish the following conversions Nitrobenzene to benzoic acid
Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reaction:

Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reaction:
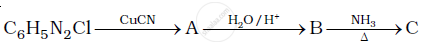
Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reaction.

Write the reactions of aliphatic primary amines with nitrous acid.
Identify 'A' and 'B' in the following reaction and rewrite the complete reaction :
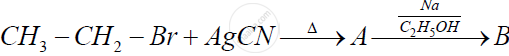
Account for the following:
Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is not preferred for preparing aromatic primary amines.
Write structures of compounds A and B in each of the following reactions: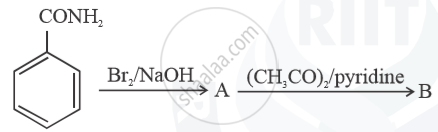
Answer the following
Explain Gabriel phthalimide synthesis.
Name the process of breaking C-X bond by ammonia in preparation of amines.
Write reactions for the preparation of ethanamine using Gabriel phthalimide synthesis.
Explain the following reaction with a suitable example.
Hofmann elimination reaction
Acetamide on reduction using Na/C2H5OH gives ____________.
Alkyl cyanides on reduction by sodium and ethanol give primary amines. This reaction is called as ____________.
Identify the product obtained, when benzamide is treated with bromine and aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Identify the product obtained when benzyl chloride undergoes ammonolysis in presence of excess ammonia followed by the reaction with two moles of methyl iodide.
Which of the following amines exhibits maximum degree of intermolecular hydrogen bonding?
____________ can be prepared exclusively by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis.
\[\ce{CH3-CN ->[Na/C2H5OH]}\]
The product formed is ____________.
Which nitrogen containing compound amongst the following would undergo Mendius reduction to furnish primary amine \[\ce{(R - NH2)}\]?
Identify the product obtained when benzamide is treated with bromine and aqueous sodium hydroxide?
The reduction of alkyl cyanide with sodium and ethanol to give primary amines is, ____________.
Identify the INCORRECT statement regarding Hofmann bromamide reaction.
Identify product B in the following reaction.
\[\ce{Aniline ->[NaNO2][HCl] A ->[KI] B}\]
Which of the following reagents is used in Hofmann's elimination reaction of amines?
Which of the following compounds is obtained when quaternary ammonium hydroxide is strongly heated?
Which of the following does NOT give carbylamine test?
Which of the following reactions does NOT yield an amine?
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Alkyl halides are insoluble in water.
Reason (R): Alkyl halides have halogen attached to sp3 hybrid carbon.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
In order to prepare a 1° amine from an alkyl halide with simultaneous addition of one \[\ce{CH2}\] group in the carbon chain, the reagent used as source of nitrogen is ______.
The best reagent for converting 2–phenylpropanamide into 2-phenylpropanamine is ______.
Best method for preparing primary amines from alkyl halides without changing the number of carbon atoms in the chain is ______.
Reduction of nitrobenzene by which of the following reagent gives aniline?
(i) \[\ce{Sn/HCl}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Fe/HCl}\]
(iii) \[\ce{H2 - Pd}\]
(iv) \[\ce{Sn/NH4OH}\]
Which of the following reactions are correct?
(i)
(ii)
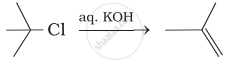
(iii)
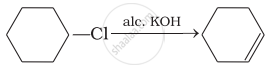
(iv)
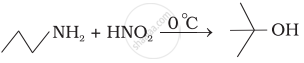
What is the product when \[\ce{C6H5CH2NH2}\] reacts with \[\ce{HNO2}\]?
How will you bring out the following conversion?

How will you carry out the following conversions?
Assertion: Hoffmann’s bromamide reaction is given by primary amines.
Reason: Primary amines are more basic than secondary amines.
The Gabriels' phthalimide synthesis is used in the synthesis of
A primary amine is formed by an amide on treatment with bromine and alkali. The primary amine has
Which of the following compound is expected to be most basic?
Write the name of the product formed by the action of LiAlH4/ether on acetamide.
Write short note on the following:
Ammonolysis
Write a short note on the following:
Ammonolysis
Write a short note on Ammonolysis.
Write short note on the following:
Ammonolysis
Write a short note on the following:
Ammonolysis
