Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Consider a gold nucleus to be a sphere of radius 6.9 fermi in which protons and neutrons are distributed. Find the force of repulsion between two protons situated at largest separation. Why do these protons not fly apart under this repulsion?
Solution
Given, radius of the sphere, R = 6.9 fermi
So, the largest separation between two protons = 2R = 13.8 fermi
Charge on a proton, q = \[1 . 6 \times {10}^{- 19} C\]
By Coulomb's Law, force of repulsion,
\[F = \frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_0}\frac{q_1 q_2}{r^2}\]
\[\Rightarrow F = 9 \times {10}^9 \times \frac{\left( 1 . 6 \times {10}^{- 19} \right)^2}{\left( 2R \right)^2} = 1 . 2 N\]
Inside the nucleus, another short-range attractive force (nuclear force) acts on the protons. That's why these protons do not fly apart due to the Coulombian repulsion.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The electrostatic force on a small sphere of charge 0.4 μC due to another small sphere of charge − 0.8 μC in air is 0.2 N.
- What is the distance between the two spheres?
- What is the force on the second sphere due to the first?
Suppose that the particle is an electron projected with velocity vx = 2.0 × 106 m s−1. If E between the plates separated by 0.5 cm is 9.1 × 102 N/C, where will the electron strike the upper plate? (|e| = 1.6 × 10−19 C, me = 9.1 × 10−31 kg)
Does the force on a charge due to another charge depend on the charges present nearby?
Two charges 2.0 × 10−6 C and 1.0 × 10−6 C are placed at a separation of 10 cm. Where should a third charge be placed, such that it experiences no net force due to these charges?
Suppose an attractive nuclear force acts between two protons which may be written as F=Ce−kr/r2. Write down the dimensional formulae and appropriate SI units of C and k.
A particle with a charge of 2.0 × 10−4 C is placed directly below and at a separation of 10 cm from the bob of a simple pendulum at rest. The mass of the bob is 100 g. What charge should the bob be given so that the string becomes loose?
A particle A with a charge of 2.0 × 10−6 C and a mass of 100 g is placed at the bottom of a smooth inclined plane of inclination 30°. Where should another particle B, with the same charge and mass, be placed on the incline so that it may remain in equilibrium?
Two particles A and B, each carrying a charge Q, are held fixed with a separation dbetween them. A particle C of mass m and charge q is kept at the middle point of the line AB. Under what conditions will the particle C execute simple harmonic motion if it is released after such a small displacement? Find the time period of the oscillations if these conditions are satisfied.
Repeat the previous problem if the particle C is displaced through a distance x along the line AB.
Two particles A and B possessing charges of +2.00 × 10−6 C and of −4.00 × 10−6 C, respectively, are held fixed at a separation of 20.0 cm. Locate the points (s) on the line AB, where (a) the electric field is zero (b) the electric potential is zero.
A point charge produces an electric field of magnitude 5.0 NC−1 at a distance of 40 cm from it. What is the magnitude of the charge?
How much work has to be done in assembling three charged particles at the vertices of an equilateral triangle, as shown in the figure?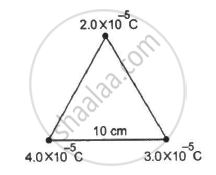
Two identical particles, each with a charge of 2.0 × 10−4 C and mass of 10 g, are kept at a separation of 10 cm and then released. What would be the speed of the particles when the separation becomes large?
Two particles of masses 5.0 g each and opposite charges of +4.0 × 10−5 C and −4.0 × 10−5 C are released from rest with a separation of 1.0 m between them. Find the speeds of the particles when the separation is reduced to 50 cm.
Two-point charges of + 0.2 µµC and -0.2 µµC are separated by 1 o8 m. What is the value of the electric field at an axial point at a distance of 0.1 m from their mid-point?
The force between two charges 0.06 m apart is 5 N. If each charge is moved towards the other by 0.01 m, then the force between them will become ____________.
SI unit of permittivity of free space is ______.
Two charge – 10c and + 10 c are placed 10 cm apart. Potential at centre of the line joining the two charge is:-
Two point charges +2 C and +6 C repel each other with a force of 12 N. If a charge of -4 C is given to each of these charges, then the force now is ______.
