Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define centre of mass.
Solution
The center of mass of a body is defined as a point where the entire mass of the body appears to be concentrated.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A high-jumper successfully clears the bar. Is it possible that his centre of mass crossed the bar from below it? Try it with appropriate figures.
In which of the following cases the centre of mass of a rod is certainly not at its centre?
(a) the density continuously increases from left to right
(b) the density continuously decreases from left to right
(c) the density decreases from left to right upto the centre and then increases
(d) the density increases from left to right upto the centre and then decreases.
Calculate the velocity of the centre of mass of the system of particles shown in figure.

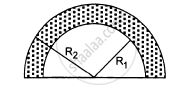
Find the centre of mass of a uniform plate having semicircular inner and outer boundaries of radii R1 and R2.
A projectile is fired with a speed u at an angle θ above a horizontal field. The coefficient of restitution of collision between the projectile and the field is e. How far from the starting point, does the projectile makes its second collision with the field?
Consider a gravity-free hall in which an experimenter of mass 50 kg is resting on a 5 kg pillow, 8 ft above the floor of the hall. He pushes the pillow down so that it starts falling at a speed of 8 ft/s. The pillow makes a perfectly elastic collision with the floor, rebounds and reaches the experimenter's head. Find the time elapsed in the process.
The ratio of weights of a man inside a lift when it is stationary and when it is going down with a uniform acceleration 'a' is 3 : 2. The value of 'a' will be ______.
(a< g, g = acceleration due to gravity)
The density of a non-uniform rod of length 1 m is given by ρ(x) = a(1 + bx2) where a and b are constants and 0 ≤ x ≤ 1. The centre of mass of the rod will be at ______.
Find the centre of mass of a uniform (a) half-disc, (b) quarter-disc.
A uniform square plate S (side c) and a uniform rectangular plate R (sides b, a) have identical areas and masses (Figure).
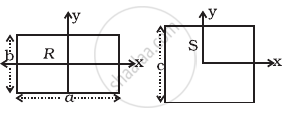
Show that
- IxR/IxS < 1
- IyR/IyS > 1
- IzR/IzS > 1
