Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Determine the current drawn from a 12 V supply with internal resistance 0.5 Ω by the infinite network shown in the figure. Each resistor has 1 Ω resistance.
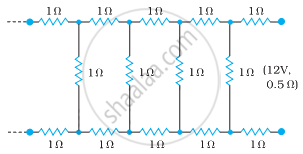
Solution
The resistance of each resistor connected in the given circuit, R = 1 Ω
Equivalent resistance of the given circuit = R’
The network is infinite. Hence, equivalent resistance is given by the relation,
∴ R' = `2 + "R'"/(("R'" + 1))`
`("R'")^2 - 2"R'" - 2 = 0`
R' = `(2 ± sqrt(4 + 8))/2`
= `(2 ± sqrt12)/2`
= `1 ± sqrt3`
Negative value of R’ cannot be accepted. Hence, equivalent resistance,
R' = `(1 + sqrt3)` = 1 + 1.73 = 2.73 Ω
Internal resistance of the circuit, r = 0.5 Ω
Hence, total resistance of the given circuit = 2.73 + 0.5 = 3.23 Ω
Supply voltage, V = 12 V
According to Ohm’s Law, current drawn from the source is given by the ratio, `12/3.23` = 3.72 A
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in electric networks. How are there rules justified?
Determine the current in each branch of the network shown in figure.

Given n resistors each of resistance R, how will you combine them to get the (i) maximum (ii) minimum effective resistance? What is the ratio of the maximum to minimum resistance?
State Kirchhoff's rules and explain on what basis they are justified.
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of (11/3) Ω?
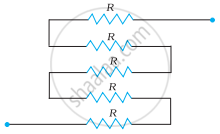
Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown in Fig.
Twelve wires, each of equal resistance r, are joined to form a cube, as shown in the figure. Find the equivalent resistance between the diagonally-opposite points a and f.

Solve the following question.
Using Kirchhoff’s rules, calculate the current through the 40 Ω and 20 Ω resistors in the following circuit.

State Kirchhoff ’s voltage rule.
State the principle of potentiometer.
How the emf of two cells are compared using potentiometer?
A copper wire of 10-6 m2 area of cross-section, carries a current of 2 A. If the number of electrons per cubic meter is 8 × 1028, calculate the current density and average drift velocity.
The instrument for the accurate measurement of the e.m.f of a cell is ______.
Kirchhoff’s second law is a consequence of law of conservation of ______.
Two cell of 1.25 V and 0.75 V are connected parallel. The effective voltage will be:-
Kirchhoff s second law is based on the law of conservation of ______
State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in the analysis of electric circuits and explain them.
The figure below shows two batteries, E1 and E2, having emfs of 18V and 10V and internal resistances of 1 Ω and 2 Ω, respectively. W1, W2 and W3 are uniform metallic wires AC, FD and BE having resistances of 8 Ω, 6 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. B and E are midpoints of the wires W1 and W2. Using Kirchhoff's laws of electrical circuits, calculate the current flowing in the wire W3:

