Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Explain the mechanism of cleaning action of soap.
Solution 1
Soap molecules form micelles around an oil droplet (dirt) in such a way that the hydrophobic parts of the stearate ions attach themselves to the oil droplet and the hydrophilic parts project outside the oil droplet. Due to the polar nature of the hydrophilic parts, the stearate ions (along with the dirt) are pulled into water, thereby removing the dirt from the cloth.

Solution 2
Soaps contain two parts: a large hydrocarbon, which is hydrophobic (water repelling), and a negatively charged head, which is hydrophillic (water attracting). In solution water molecules, being polar in nature, surround the ions and not the organic part of the molecule. When a soap is dissolved in water, the molecules gather together as clusters, called micelles. The tails stick inward and the head tward. The hydrocarbon tail attaches itself to oily dirt. When water is agitated, the oily dirt tends to lift off from the dirty surface and dissociate into fragments. The solution now contains small globules of oil-surrounded detergent molecules. The negatively charged heads present in water prevent the small globules from coming together and forming aggregates. Thus the oily dirt is removed from the object.
Solution 3
The mechanism of cleansing action of soap:
- A molecule of soap has two dissimilar ends. The hydrophobic end of the hydrocarbon chain is water repellent, while the hydrophilic end is polar and water soluble due to presence of carboxylate anion. Thus a soap molecule may be represented as:

- When a soap is dissolved in water, many molecules come together and form a group called a micelle because their hydrocarbon chains come together and the polar ends are projected outward.
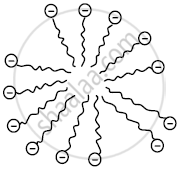
Micelle formation - When a cloth with a spot of oil and dirt is soaked into the soap solution, soap dissolves a tiny oil droplet by the hydrophobic end in the middle of the micelle. Due to the outwardly projected polar ends, these micelles dissolve in water and are washed away. Thus the clothes get cleaned.
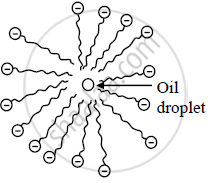
Oil droplet in the middle of the micelle
Notes
Students should refer to the answer according to their question and preferred marks.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain cationic detergents.
What is a soap ?
Write the chemical equation for preparing sodium soap from Glyceryl palmitate . Structural formulae of the compounds are given below.
(C15H31COO)3C3H5 – Glyceryl palmitate
Write the chemical equation for preparing sodium soap from glyceryl oleate . Structural formulae of the compounds are given below.
(C17H32COO)3C3H5 – Glyceryl oleate
Why do soaps not work in hard water?
Can you use soaps and synthetic detergents to check the hardness of water?
Explain the mechanism of cleansing action of soaps.
Write balanced chemical equations for the action of hydrogen bromide on styrene in the presence of a peroxide
How soap is prepared?
Which of the following enhances leathering property of soap?
Glycerol is added to soap. It functions ______.
What is a soft soap?
If soap has high alkali content it irritates skin. How can the amount of excess alkali be determined? What can be the source of excess alkali?
Why is it safer to use soap from the environmental point of view?
What is the side product of soap industry? Give reactions showing soap formation.
What is the difference between bathing soap and washing soaps?
How are transparent soaps manufactured?
What are fillers and what role these fillers play in soap?
Match the soaps given in Column I with items given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Soap chips | (a) dried miniature soap bubbles |
| (ii) Soap granules | (b) small broken pieces of soap formed from melted soaps |
| (iii) Soap powder | (c) soap powder + abrasives + builders \[\ce{(Na2CO3,Na3PO4)}\] |
| (iv) Scouring soap | (d) soap powder + builders like \[\ce{Na2CO3}\] and \[\ce{Na3PO4}\] |
Match the detergents given in Column I with their uses given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
(i) 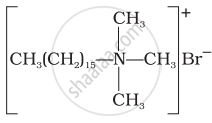 |
(a) Dishwashing powder |
(ii) 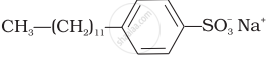 |
(b) Laundry soap |
| (iii) \[\ce{C17H33CO\overset{-}{O}\overset{+}{N}a + Na2CO3 + Rosin}\] | (c) Hair conditioners |
| (iv) \[\ce{CH3(CH2)16COO(CH2CH2O)nCH2CH2OH}\] | (d) Toothpaste |
Assertion: Transparent soaps are made by dissolving soaps in ethanol.
Reason: Ethanol makes things invisible.
Assertion: Sodium chloride is added to precipitate soap after saponification.
Reason: Hydrolysis of esters of long-chain fatty acids by alkali produces soap in colloidal form.
Green chemistry in day-to-day life is in the use of ______.
Self-cleansing windows are example of the ______.
