Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find all the three angles of the ΔABC
Solution
∠A + ∠B = ∠ACD ...(An exterior angle of a triangle is sum of its interior opposite angles)
x + 35 + 2x – 5 = 4x – 15
3x + 30 = 4x – 15
30 + 15 = 4x – 3x
45° = x
∠A = x + 35°
= 45° + 35°
= 80°
∠B = 2x – 5
= 2(45°) – 5°
= 90° – 5°
= 85°
∠ACD = 4x – 15
= 4(45°) – 15°
= 180° – 15°
= 165°
∠ACB = 180° – ∠ACD
= 180° – 165°
= 15°
∠A = 80°, ∠B = 85° and ∠C = 15°.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
AB is a line segment. P and Q are points on opposite sides of AB such that each of them is equidistant from the points A and B (See Fig. 10.26). Show that the line PQ is perpendicular bisector of AB.

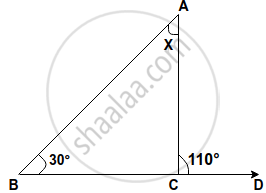
Compute the value of x in the following figure:
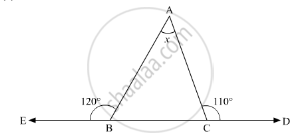
In the given figure, AB || DE. Find ∠ACD.

State exterior angle theorem.
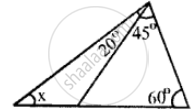
Calculate the unknown marked angles of the following figure :
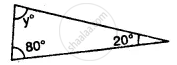
In the following, find the marked unknown angle:
Can a triangle together have the following angles?
33°, 74° and 73°
Find, giving a reason, the unknown marked angles, in a triangle drawn below:
In figure, PQ ⊥ RQ, PQ = 5 cm and QR = 5 cm. Then ∆PQR is ______.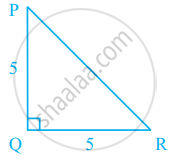
Can we have two acute angles whose sum is a reflex angle? Why or why not?
