Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Form the differential equation of the family of circles touching the y-axis at the origin.
Solution
The centre of the circle touching the y-axis at origin lies on the x-axis.
Let (a, 0) be the centre of the circle.
Since it touches the y-axis at origin, its radius is a.
Now, the equation of the circle with centre (a, 0) and radius (a) is
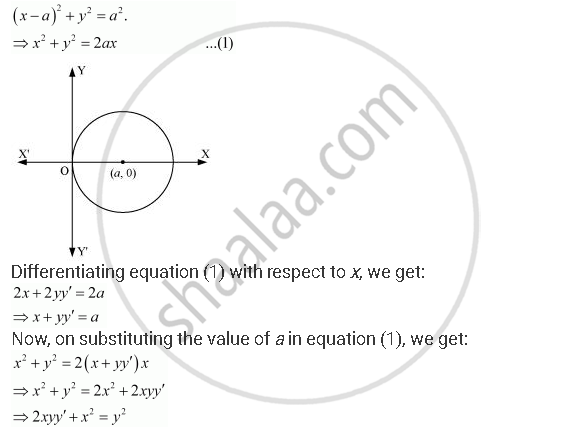
This is the required differential equation.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Form the differential equation of the family of hyperbolas having foci on x-axis and centre at origin.
Which of the following differential equations has y = c1 ex + c2 e–x as the general solution?
(A) `(d^2y)/(dx^2) + y = 0`
(B) `(d^2y)/(dx^2) - y = 0`
(C) `(d^2y)/(dx^2) + 1 = 0`
(D) `(d^2y)/(dx^2) - 1 = 0`
Which of the following differential equation has y = x as one of its particular solution?
A. `(d^2y)/(dx^2) - x^2 (dy)/(dx) + xy = x`
B. `(d^2y)/(dx^2) + x dy/dx + xy = x`
C. `(d^2y)/(dx^2) - x^2 dy/dx + xy = 0`
D. `(d^2y)/(dx^2) + x dy/dx + xy = 0`
Form the differential equation representing the family of curves given by (x – a)2 + 2y2 = a2, where a is an arbitrary constant.
For the curve y = 5x – 2x3, if x increases at the rate of 2 units/sec, then find the rate of change of the slope of the curve when x = 3
Show that the family of curves for which `dy/dx = (x^2+y^2)/(2x^2)` is given by x2 - y2 = cx
Form the differential equation from the following primitive where constants are arbitrary:
y2 = 4ax
Form the differential equation from the following primitive where constants are arbitrary:
xy = a2
Form the differential equation corresponding to y2 = a (b − x2) by eliminating a and b.
Form the differential equation corresponding to (x − a)2 + (y − b)2 = r2 by eliminating a and b.
Form the differential equation of the family of curves represented by the equation (a being the parameter):
(2x + a)2 + y2 = a2
Form the differential equation of the family of curves represented by the equation (a being the parameter):
(2x − a)2 − y2 = a2
Form the differential equation of the family of curves represented by the equation (a being the parameter):
(x − a)2 + 2y2 = a2
Represent the following families of curves by forming the corresponding differential equations (a, b being parameters):
x2 − y2 = a2
Represent the following families of curves by forming the corresponding differential equations (a, b being parameters):
y2 = 4ax
Represent the following families of curves by forming the corresponding differential equations (a, b being parameters):
(x − a)2 − y2 = 1
Represent the following families of curves by forming the corresponding differential equations (a, b being parameters):
Represent the following families of curves by forming the corresponding differential equations (a, b being parameters):
y = ax3
Find the equation of a curve passing through the point (0, 0) and whose differential equation is \[\frac{dy}{dx} = e^x \sin x\]
Find one-parameter families of solution curves of the following differential equation:-
\[\frac{dy}{dx} - \frac{2xy}{1 + x^2} = x^2 + 2\]
Find one-parameter families of solution curves of the following differential equation:-
\[\frac{dy}{dx} + y \cos x = e^{\sin x} \cos x\]
Write the order of the differential equation representing the family of curves y = ax + a3.
The differential equation which represents the family of curves y = eCx is
The family of curves in which the sub tangent at any point of a curve is double the abscissae, is given by
Form the differential equation representing the family of curves y = mx, where m is an arbitrary constant.
Form the differential equation of the family of ellipses having foci on y-axis and centre at the origin.
Find the differential equation of the family of curves y = Ae2x + B.e–2x.
The differential equation representing the family of curves y = A sinx + B cosx is ______.
Form the differential equation by eliminating A and B in Ax2 + By2 = 1
Find the equation of a curve passing through (2, 1) if the slope of the tangent to the curve at any point (x, y) is `(x^2 + y^2)/(2xy)`.
Find the equation of a curve passing through the point (1, 1). If the tangent drawn at any point P(x, y) on the curve meets the co-ordinate axes at A and B such that P is the mid-point of AB.
Family y = Ax + A3 of curves is represented by the differential equation of degree ______.
The differential equation `y ("d"y)/("d"x) + "c"` represents: ______.
The curve for which the slope of the tangent at any point is equal to the ratio of the abcissa to the ordinate of the point is ______.
From the differential equation of the family of circles touching the y-axis at origin
Form the differential equation of family of circles having centre on y-axis and raduis 3 units
