Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If the intensity of sound is doubled, by how many decibels does the sound level increase?
Solution
Let the intensity of the sound be I and \[\beta_1\] be the sound level. If the intensity of the sound is doubled, then its sound level becomes 2I.
Sound level \[\beta_1\] is given by ,\[\beta_1 = 10 \log_{10} \frac{I}{I_0}\],
where I0 is the constant reference intensity.
When the intensity doubles, the sound level is given by:
\[\beta_2 = 10 \log_{10} \frac{2I}{I_0}\].
According to the question,
\[ \beta_2 - \beta_1 = 10 \log\left( \frac{2I}{I} \right)\]
\[ = 10 \times 0 . 3010 = 3 \text{ dB }\]
The sound level is increased by 3 dB.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If you are walking on the moon, can you hear the sound of stones cracking behind you? Can you hear the sound of your own footsteps?
The voice of a person, who has inhaled helium, has a remarkably high pitch. Explain on the basis of resonant vibration of vocal cord filled with air and with helium.
When we clap our hands, the sound produced is best described by Here p denotes the change in pressure from the equilibrium value.
Two sound waves move in the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitudes of the waves are equal but the wavelength of the first wave is double the second. Let the average power transmitted across a cross section by the first wave be P1 and that by the second wave be P2. Then
A tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz is vibrated with a sonometer wire and 6 beats per second are heard. The beat frequency reduces if the tension in the string is slightly increased. The original frequency of vibration of the string is
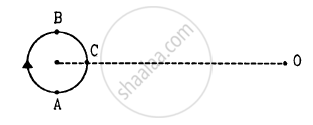
A small source of sounds moves on a circle as shown in figure and an observer is sitting at O. Let \[v_1, v_2, v_3\] be the frequencies heard when the source is at A, B and C respectively.
An electrically maintained tuning fork vibrates with constant frequency and constant amplitude. If the temperature of the surrounding air increases but pressure remains constant, the produced will have
(a) larger wavelength
(b) larger frequency
(c) larger velocity
(d) larger time period.
The fundamental frequency of a vibrating organ pipe is 200 Hz.
(a) The first overtone is 400 Hz.
(b) The first overtone may be 400 Hz.
(c) The first overtone may be 600 Hz.
(d) 600 Hz is an overtone.
A sound wave frequency 100 Hz is travelling in air. The speed of sound in air is 350 m s−1. (a) By how much is the phase changed at a given point in 2.5 ms? (b) What is the phase difference at a given instant between two points separated by a distance of 10.0 cm along the direction of propagation?
Two point sources of sound are kept at a separation of 10 cm. They vibrate in phase to produce waves of wavelength 5.0 cm. What would be the phase difference between the two waves arriving at a point 20 cm from one source (a) on the line joining the sources and (b) on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the sources?
A string, fixed at both ends, vibrates in a resonant mode with a separation of 2⋅0 cm between the consecutive nodes. For the next higher resonant frequency, this separation is reduced to 1⋅6 cm. Find the length of the string.
A particular guitar wire is 30⋅0 cm long and vibrates at a frequency of 196 Hz when no finger is placed on it. The next higher notes on the scale are 220 Hz, 247 Hz, 262 Hz and 294 Hz. How far from the end of the string must the finger be placed to play these notes?
The noise level in a classroom in absence of the teacher is 50 dB when 50 students are present. Assuming that on the average each student output same sound energy per second, what will be the noise level if the number of students is increased to 100?
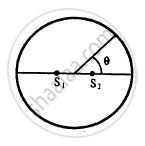
Figure shown two coherent sources S1 and S2 which emit sound of wavelength λ in phase. The separation between the sources is 3λ. A circular wire of large radius is placed in such way that S1,S2 is at the centre of the wire. Find the angular positions θ on the wire for which constructive interference takes place.
Two sources of sound S1 and S2 vibrate at same frequency and are in phase. The intensity of sound detected at a point P as shown in the figure is I0. (a) If θ equals 45°, what will be the intensity of sound detected at this point if one of the sources is switched off? (b) What will be the answer of the previous part if θ = 60°?
A tuning fork produces 4 beats per second with another tuning fork of frequency 256 Hz. The first one is now loaded with a little wax and the beat frequency is found to increase to 6 per second. What was the original frequency of the tuning fork?
A train running at 108 km h−1 towards east whistles at a dominant frequency of 500 Hz. Speed of sound in air is 340 m/s. What frequency will a passenger sitting near the open window hear? (b) What frequency will a person standing near the track hear whom the train has just passed? (c) A wind starts blowing towards east at a speed of 36 km h−1. Calculate the frequencies heard by the passenger in the train and by the person standing near the track.
A person standing on a road sends a sound signal to the driver of a car going away from him at a speed of 72 km h−1. The signal travelling at 330 m s−1 in air and having a frequency of 1600 Hz gets reflected from the body of the car and returns. Find the frequency of the reflected signal as heard by the person.
The speed of a wave in a string is 20 m/s and the frequency is 50 Hz. The phase difference between two points on the string 10 cm apart will be ______.
