Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A particular guitar wire is 30⋅0 cm long and vibrates at a frequency of 196 Hz when no finger is placed on it. The next higher notes on the scale are 220 Hz, 247 Hz, 262 Hz and 294 Hz. How far from the end of the string must the finger be placed to play these notes?
Solution
Given:
Length of the guitar wire (L1) = 30.0 cm = 0.30 m
Frequency, when no finger is placed on it, (f1) =196 Hz
And (f2) =220 Hz, (f3) = 247 Hz, (f4) = 262 Hz and (f5) = 294 Hz
The velocity is constant for a medium.
We have:
\[f \propto \left( \frac{1}{L} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \frac{f_1}{f_2} = \frac{L_2}{L_1}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{196}{220} = \frac{L_2}{0 . 3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow L_2 = \frac{196 \times 0 . 3}{220} = 0 . 267 m\]
\[ \Rightarrow L_2 = 26 . 7 cm\]
Again,
\[f_3 = 247 Hz\]
\[\Rightarrow \frac{f_3}{f_1} = \frac{L_1}{L_3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{247}{196} = \frac{0 . 3}{L_3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow L_3 = 196 \times \frac{0 . 3}{247} = 0 . 238 m\]
\[ \Rightarrow L_3 = 23 . 8 cm\]
\[Similarly, L_4 = 196 \times \frac{0 . 3}{262} = 0 . 224 m\]
\[ \Rightarrow L_4 = 22 . 4 cm\]
\[And, L_5 = 20 \text{ cm }\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The wavelengths of two sound waves in air are `81/173`m and `81/170`m. They produce 10 beats per second. Calculate the velocity of sound in air
A wave is represented by an equation \[y = c_1 \sin \left( c_2 x + c_3 t \right)\] In which direction is the wave going? Assume that \[c_1 , c_2\] \[c_3\] are all positive.
Two loudspeakers are arranged facing each other at some distance. Will a person standing behind one of the loudspeakers clearly hear the sound of the other loudspeaker or the clarity will be seriously damaged because of the 'collision' of the two sounds in between?
The voice of a person, who has inhaled helium, has a remarkably high pitch. Explain on the basis of resonant vibration of vocal cord filled with air and with helium.
Two sound waves move in the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitudes of the waves are equal but the wavelength of the first wave is double the second. Let the average power transmitted across a cross section by the first wave be P1 and that by the second wave be P2. Then
When two waves with same frequency and constant phase difference interfere,
An electrically maintained tuning fork vibrates with constant frequency and constant amplitude. If the temperature of the surrounding air increases but pressure remains constant, the produced will have
(a) larger wavelength
(b) larger frequency
(c) larger velocity
(d) larger time period.
A man stands before a large wall at a distance of 50.0 m and claps his hands at regular intervals. Initially, the interval is large. He gradually reduces the interval and fixes it at a value when the echo of a clap merges every 3 seconds, find the velocity of sound in air.
Ultrasonic waves of frequency 4.5 MHz are used to detect tumour in soft tissue. The speed of sound in tissue is 1.5 km s−1 and that in air is 340 m s−1. Find the wavelength of this ultrasonic wave in air and in tissue.
The sound level at a point 5.0 m away from a point source is 40 dB. What will be the level at a point 50 m away from the source?
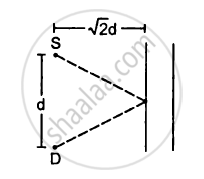
A source S and a detector D are placed at a distance d apart. A big cardboard is placed at a distance \[\sqrt{2}d\] from the source and the detector as shown in figure. The source emits a wave of wavelength = d/2 which is received by the detector after reflection from the cardboard. It is found to be in phase with the direct wave received from the source. By what minimum distance should the cardboard be shifted away so that the reflected wave becomes out of phase with the direct wave?
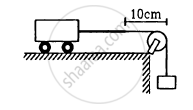
A heavy string is tied at one end to a movable support and to a light thread at the other end as shown in following figure. The thread goes over a fixed pulley and supports a weight to produce a tension. The lowest frequency with which the heavy string resonates is 120 Hz. If the movable support is pushed to the right by 10 cm so that the joint is placed on the pulley, what will be the minimum frequency at which the heavy string can resonate?
A tuning fork of frequency 256 Hz produces 4 beats per second with a wire of length 25 cm vibrating in its fundamental mode. The beat frequency decreases when the length is slightly shortened. What could be the minimum length by which the wire we shortened so that it produces no beats with the tuning fork?
A train running at 108 km h−1 towards east whistles at a dominant frequency of 500 Hz. Speed of sound in air is 340 m/s. What frequency will a passenger sitting near the open window hear? (b) What frequency will a person standing near the track hear whom the train has just passed? (c) A wind starts blowing towards east at a speed of 36 km h−1. Calculate the frequencies heard by the passenger in the train and by the person standing near the track.
A boy riding on a bicycle going at 12 km h−1 towards a vertical wall whistles at his dog on the ground. If the frequency of the whistle is 1600 Hz and the speed of sound in air is 330 m s−1, find (a) the frequency of the whistle as received by the wall (b) the frequency of the reflected whistle as received by the boy.
During propagation of a plane progressive mechanical wave ______.
- all the particles are vibrating in the same phase.
- amplitude of all the particles is equal.
- particles of the medium executes S.H.M.
- wave velocity depends upon the nature of the medium.
A transverse wave is represented by y = 2sin (ωt - kx) cm. The value of wavelength (in cm) for which the wave velocity becomes equal to the maximum particle velocity, will be ______.
