Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In ∆ABC, ∠A = 60°. Prove that BC2 = AB2 + AC2 − AB . AC.
Solution
In ΔABC, in which ∠A is an acute angle with 60°.

`sin 60^o = (CD)/(AC)=sqrt3/2`
`⇒ CD = sqrt3/2AC`.................(1)
`cose 60^o = (AD)/(AC)=1/2`
`⇒ AD = 1/2 AC`
Now apply Pythagoras' theorem in triangle BCD
`BC^2=CD^2+BD^2`
`= CD^2 +(AB-AD)^2`
`= (sqrt3/2AC)^2+AB^2+(1/2AC)^2-2AB1/2AC`
`=AC^2+AB^2-AB.AC`
Hence `BC^2=AB^2+AC^2-AB.AC`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In an isosceles ΔABC, the base AB is produced both the ways to P and Q such that AP × BQ = AC2. Prove that ΔAPC ~ ΔBCQ.
D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a ΔABC. In each of the following cases, determine whether DE║BC or not.
AB = 11.7cm, AC = 11.2cm, BD = 6.5cm and AE = 4.2cm.
In a ΔABC, AD is the bisector of ∠A.
If AB = 5.6cm, AC = 4cm and DC = 3cm, find BC.

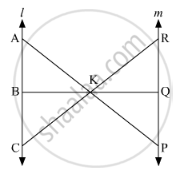
In the given figure, l || m
(i) Name three pairs of similar triangles with proper correspondence; write similarities.
(ii) Prove that
Corresponding sides of two triangles are in the ratio 2 : 3. If the area of the smaller triangle is 48 cm2, determine the area of the larger triangle.
In ∆ABC, given that AB = AC and BD ⊥ AC. Prove that BC2 = 2 AC. CD
If ABC and DEF are similar triangles such that ∠A = 57° and ∠E = 73°, what is the measure of ∠C?
ABCD is a trapezium such that BC || AD and AD = 4 cm. If the diagonals AC and BD intersect at O such that \[\frac{AO}{OC} = \frac{DO}{OB} = \frac{1}{2}\], then BC =
∆ABC ∼ ∆DEF. If BC = 3 cm, EF = 4 cm and ar(∆ABC) = 54 cm2, then ar(∆DEF) =
In the given figure the measure of ∠D and ∠F are respectively