Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In quadrilateral ABCD, the diagonals AC and BD intersect each other at point O. If AO = 2CO and BO = 2DO; show that: OA × OD = OB × OC.
Solution
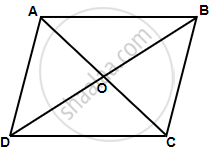
Since AO = 2CO and BO = 2DO,
`(AO)/(CO) = 2/1 = (BO)/(DO)`
So, OA × OD = OB × OC
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
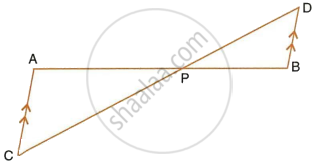
In the figure, given below, straight lines AB and CD intersect at P; and AC || BD. Prove that: If BD = 2.4 cm, AC = 3.6 cm, PD = 4.0 cm and PB = 3.2 cm; find the lengths of PA and PC.
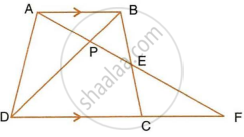
In a trapezium ABCD, side AB is parallel to side DC; and the diagonals AC and BD intersect each other at point P. Prove that : PA x PD = PB x PC.
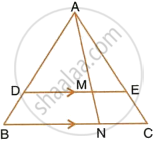
In the given figure, DE || BC, AE = 15 cm, EC = 9 cm, NC = 6 cm and BN = 24 cm. Find lengths of ME and DM.
In ΔABC, angle ABC is equal to twice the angle ACB, and bisector of angle ABC meets the opposite side at point P. Show that: CB : BA = CP : PA
In the following figure, XY is parallel to BC, AX = 9 cm, XB = 4.5 cm and BC = 18 cm.

Find : `(YC)/(AC)`
In the following figure, ABCD to a trapezium with AB || DC. If AB = 9 cm, DC = 18 cm, CF = 13.5 cm, AP = 6 cm and BE = 15 cm.
Calculate:
- EC
- AF
- PE
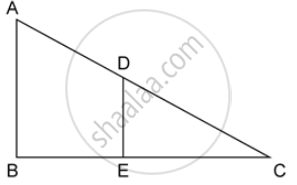
In the given figure, AB and DE are perpendiculars to BC.
Prove that : ΔABC ~ ΔDEC
Two isosceles triangle have equal vertical angles and their areas are in the ratio of 36 : 25. Find the ratio between their corresponding heights.
Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
If area (ΔABC) = 9 cm2, area (ΔDEF) = 64 cm2 and BC = 5·1 cm find AB.
Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
If area (ΔABC) = 36 cm2, area (ΔDEf) = 64 cm2 and DE = 6.2 cm, find AB.
