Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
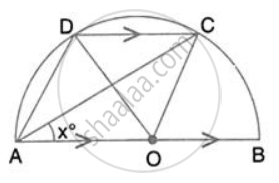
In the given figure, AOB is a diameter and DC is parallel to AB. If ∠ CAB = xo ; find (in terms of x) the values of: ∠ DOC.
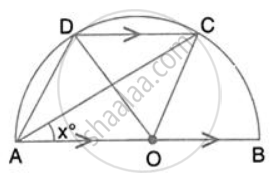
Solution
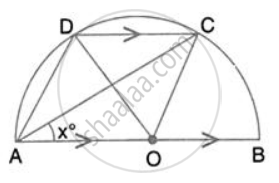
∠OCD = ∠COB = 2x (Alternate angles)
In ∠OCD, OC = OD
∴ ∠ODC = ∠OCD = 2x
By angle sum property of ∆OCD,
∠DOC = 180° - 2x - 2x = 180° - 4x
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
AB is the diameter of the circle with centre O. OD is parallel to BC and ∠AOD = 60°. Calculate the numerical values of :
- ∠ABD,
- ∠DBC,
- ∠ADC.
In a regular pentagon ABCDE, inscribed in a circle; find ratio between angle EDA and angle ADC.
The figure shows a circle with centre O. AB is the side of regular pentagon and AC is the side of regular hexagon. Find the angles of triangle ABC.

In the given figure, AB is the diameter of the circle with centre O.
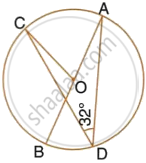
If ∠ADC = 32°, find angle BOC.
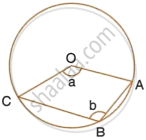
The figure given below, shows a circle with centre O. Given : ∠AOC = a and ∠ABC = b.
-
Find the relationship between a and b.
-
Find the measure of angle OAB, if OABC is a parallelogram.
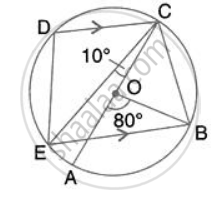
In the given figure, AC is the diameter of circle, centre O. CD and BE are parallel. Angle AOB = 80o and angle ACE = 10o. Calculate: Angle CED.
In the given figure, AOB is a diameter and DC is parallel to AB. If ∠ CAB = xo ; find (in terms of x) the values of: ∠ DAC
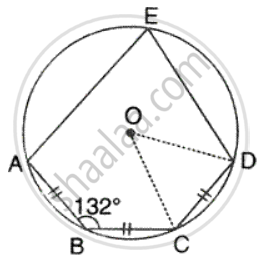
In the given figure, AB = BC = CD and ∠ABC = 132° . Calcualte: ∠ COD.
In the given Figure, ABC is a triangle in which ∠BAC = 30°. Show that BC is the radius of the circumcircle of A ABC, whose center is O.
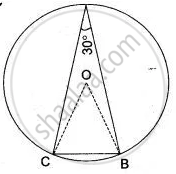
If O is the circumcentre of a Δ ABC and OD ⊥ BC, prove that ∠ BOD = ∠A.
