Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Is the area of your belt the same as the area of the postcard? Why or why not?
Solution
Area of the belt of 3 cm wide strip = length x breadth
= 3 × 42
= 126 square cm
Yes, this is equal to the area of the postcard.
In fact, area of all the belts would be equal to the area of the postcard; because every part of the postcard is being used in making a belt.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
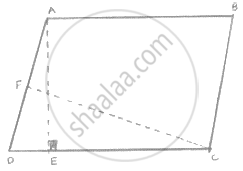
In fig below, ABCD is a parallelogram, AE ⊥ DC and CF ⊥ AD. If AB = 16 cm, AE = 8
cm and CF = 10 cm, find AD.
If ABCD is a parallelogram, then prove that
𝑎𝑟 (Δ𝐴𝐵𝐷) = 𝑎𝑟 (Δ𝐵𝐶𝐷) = 𝑎𝑟 (Δ𝐴𝐵𝐶) = 𝑎𝑟 (Δ𝐴𝐶𝐷) = `1/2` 𝑎𝑟 (||𝑔𝑚 𝐴𝐵𝐶𝐷) .
In the below Fig, ABC and ABD are two triangles on the base AB. If line segment CD is
bisected by AB at O, show that ar (Δ ABC) = ar (Δ ABD)

A point D is taken on the side BC of a ΔABC such that BD = 2DC. Prove that ar(Δ ABD) =
2ar (ΔADC).
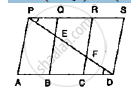
In below fig., PSDA is a parallelogram in which PQ = QR = RS and AP || BQ || CR. Prove
that ar (Δ PQE) = ar (ΔCFD).
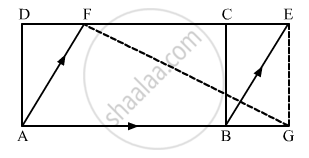
In the given figure, ABCD is a rectangle with sides AB = 10 cm and AD = 5 cm. Find the area of ΔEFG.
ABC is a triangle in which D is the mid-point of BC. E and F are mid-points of DC and AErespectively. IF area of ΔABC is 16 cm2, find the area of ΔDEF.
Two parallelograms are on the same base and between the same parallels. The ratio of their areas is
Let ABC be a triangle of area 24 sq. units and PQR be the triangle formed by the mid-points of the sides of Δ ABC. Then the area of ΔPQR is
A, B, C, D are mid-points of sides of parallelogram PQRS. If ar (PQRS) = 36 cm2, then ar (ABCD) =
The figure obtained by joining the mid-points of the adjacent sides of a rectangle of sides 8 cm and 6 cm is ______.
Medians of ΔABC intersect at G. If ar (ΔABC) = 27 cm2, then ar (ΔBGC) =
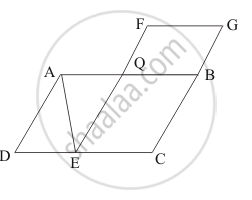
In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. If AB = 12 cm, AE = 7.5 cm, CF = 15 cm, then AD =

In the given figure, ABCD and FECG are parallelograms equal in area. If ar (ΔAQE) = 12 cm2, then ar (||gm FGBQ) =
The perimeter of a triangle ABC is 37 cm and the ratio between the lengths of its altitudes be 6: 5: 4. Find the lengths of its sides.
Let the sides be x cm, y cm, and (37 - x - y) cm. Also, let the lengths of altitudes be 6a cm, 5a cm, and 4a cm.
Find the area of a rectangle whose length = 8.5 m breadth = 5 m.
The side of a square field is 16 m. What will be increase in its area, if each of its sides is doubled?
In the same way, find the area of piece B.
This stamp has an area of 4 square cm. Guess how many such stamps will cover this big rectangle.

What is the area of the rectangle? ________ square cm
Measure the length of the floor of your classroom in meters. Also, measure the width.
- So how many children can sit in one square meter?
Look at the table. If you were to write the area of each of these which column would you choose? Make a (✓).
| Square cm |
Square meter |
Square km |
|
| Handkerchief | ✓ | ||
| Sari | |||
| Page of your book | |||
| School land | |||
| Total land of a city | |||
| Door of your classroom | |||
| Chair seat | |||
| Blackboard | |||
| Indian flag | |||
| Land over which a river flows |
Is the area of both your footprints the same?
Find the area of the following figure by counting squares:

Find the area of the following figure by counting squares:

Find the area of the following figure by counting squares:

