Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Match the reactions given in Column I with the types of reactions given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) | 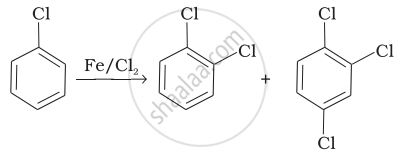 |
(a) Nucleophilic aromatic substitution |
| (ii) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - CH = CH2 + HBr -> CH3 - CH - CH3}\\ \phantom{............................}|\phantom{}\\ \phantom{.............................}\ce{Br}\phantom{} \end{array}\] |
(b) Electrophilic aromatic substitution |
| (iii) | 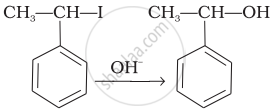 |
(c) Saytzeff elimination |
| (iv) | 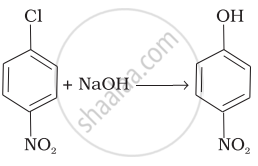 |
(d) Electrophilic addition |
| (v) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 CH2 CH CH3 ->[alc.KOH] CH3 CH = CH CH3}\\ \phantom{}|\phantom{..........................}\\ \phantom{}\ce{Br}\phantom{........................} \end{array}\] |
(e) Nucleophilic substitution (SN1) |
Solution
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) |  |
(b) Electrophilic aromatic substitution |
| (ii) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - CH = CH2 + HBr -> CH3 - CH - CH3}\\ \phantom{............................}|\phantom{}\\ \phantom{.............................}\ce{Br}\phantom{} \end{array}\] |
(d) Electrophilic addition |
| (iii) |  |
(e) Nucleophilic substitution (SN1) |
| (iv) |  |
(a) Nucleophilic aromatic substitution |
| (v) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 CH2 CH CH3 ->[alc.KOH] CH3 CH = CH CH3}\\ \phantom{}|\phantom{..........................}\\ \phantom{}\ce{Br}\phantom{........................} \end{array}\] |
(c) Saytzeff elimination |
Explanation:
(i) In this reaction, an electrophile CF attacks on to the benzene ring and substitution takes place.
(ii) In this reaction, addition of \[\ce{HBr}\] takes place on to the doubly bonded carbons of propene in accordance with Markownikoff’s rule and electrophilic addition takes place.
(iii) In this reaction, the reactant is secondary halide. Here, halogen atom is substituted by hydroxyl ion. As it is secondary halide so it follows SN1 mechanism.
(iv) In this reaction, halogen atom is directly bonded to aromatic ring. So, it is nucleophilic aromatic substitution as OH– group has substituted halogen of given compound.
(v) It is an elimination reaction. It follows Saytzeff elimination rule.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How do you convert the following:
Ethanol to propanenitrile
Write the main products when methyl chloride is treated with AgCN.
Out of 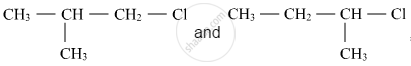 , which is more reactive towards SN1 reaction and why?
, which is more reactive towards SN1 reaction and why?
In the following pair of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes a faster SN1 reaction?
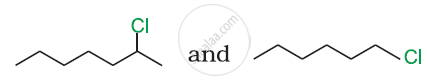
Answer the following question.
Write one stereochemical difference between SN1 and SN2 reactions.
Which of the following compounds will give a racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by OH ion?
1-Bromoethane, 1-Bromopropane, 1-Bromobutane, Bromobenzene
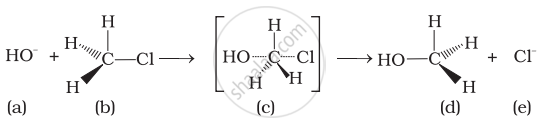
Which of the statements are correct about above reaction?
(i) (a) and (e) both are nucleophiles.
(ii) In (c) carbon atom is sp3 hybridised.
(iii) In (c) carbon atom is sp2 hybridised.
(iv) (a) and (e) both are electrophiles.
Which of the compounds will react faster in SN1 reaction with the –OH ion?
\[\ce{CH3-CH2-Cl}\] or \[\ce{C6H5-CH2-Cl}\]
Retention of configuration is observed in ______.
Complete the reaction with the main product formed:

