Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of suspended coil type moving coil galvanometer.
Solution 1
Suspended type of moving coil galvanometer:-

PQRS = Rectangular coil
W = Thin phosphor bronze wire suspension
M = Plane mirror
H = Helical spring
C = Soft iron cylinder
I = Current through the coil
Solution 2
Moving Coil Galvanometer -

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
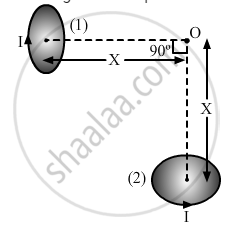
Two very small identical circular loops, (1) and (2), carrying equal currents I are placed vertically (with respect to the plane of the paper) with their geometrical axes perpendicular to each other as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field produced at the point O.
A current loop of arbitrary shape lies in a uniform magnetic field B. Show that the net magnetic force acting on the loop is zero.
A rectangular loop of sides 20 cm and 10 cm carries a current of 5.0 A. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.20 T exists parallel to the longer side of the loop. (a) What is the force acting on the loop? (b) What is the torque acting on the loop?
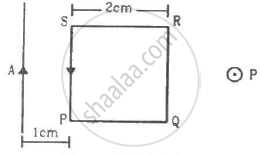
A square loop PQRS carrying a current of 6.0 A is placed near a long wire carrying 10 A as shown in figure. (a) Show that the magnetic force acting on the part PQ is equal and opposite to the part RS. (b) Find the magnetic force on the square loop.
A current-carrying circular coil of 100 turns and radius 5.0 cm produces a magnetic field of 6.0 × 10−5 T at its centre. Find the value of the current.
Derive the expression for the torque acting on a current-carrying loop placed in a magnetic field.
A moving coil galvanometer has been fitted with a rectangular coil having 50 turns and dimensions 5 cm × 3 cm. The radial magnetic field in which the coil is suspended is of 0.05 Wb/m2. The torsional constant of the spring is 1.5 × 10−9 Nm/degree. Obtain the current required to be passed through the galvanometer so as to produce a deflection of 30°.
A Rectangular coil of 10 turns, each of area 0.05 m2, is suspended freely in a uniform magnetic field of induction 0.01 T. A current of 30 µA is passed through it.
(i) What is the magnetic moment of the coil?
(ii) What is the maximum torque experienced by the coil?
Derive the expression for the torque on a current-carrying coil in a magnetic field.
A rectangular coil of length 0.12 m and width 0.1 m having 100 turns of wire is suspended vertically in a uniform magnetic field of strength 0.4 Wb/m2. The coil carries a current of 2.5 A. If the plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° with the direction of the field, the torque required to keep the coil in stable equilibrium will be ____________.
Torque acting on a rectangular coil carrying current 'l' situated parallel to magnetic field of induction 'B', having number of turns 'n' and area 'A' is ______.
A 100 turn rectangular coil measuring 0.02 m x 0.06 m of an ammeter is in a magnetic field of induction 0.4 tesla. The torsional constant of the suspension fibre is 5 x 10-7 newton x metre/degree. The maximum reading of the ammeter corresponds to a deflection of the coil through 30°. If the magnetic field is radial, then the maximum current that can be measured with this ammeter is ____________.
A small cylindrical soft iron piece is kept in a galvanometer so that
A rectangular coil has 200 turns each of area 50 cm2 . It is capable of rotation about an axis joining the mid points of two opposite sides. When a current of 10 A is passed through it while its plane is at right angles to a uniform magnetic field, it experiences a torque of 5 Nm. The magnetic field will be ____________.
Two galvanometers 'G1' and 'G2' require 2 mA and 3 mA respectively to produce the same deflection. Then _______.
If number of turns in moving coil galvanometer becomes half, then the deflection for the same current will become ____________.
The current flowing through moving coil galvanometer is 20% of the current to be measured. The resistance of moving coil galvanometer is 48 `Omega`, then shunt required is ____________.
An ammeter is obtained by shunting 'n' `Omega` galvanometer with 'n' `Omega` resistance. The additional shunt required to be connected across it to double the range is ____________.
A circular coil of 20 turns and radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.10 T normal to the plane of the coil. If the current in the coil is 5.0 A, what is the
(a) total torque on the coil,
(b) total force on the coil,
(c) average force on each electron in the coil due to the magnetic field?
(The coil is made of copper wire of cross-sectional area 10–5 m2, and the free electron density in copper is given to be about 1029 m–3.)
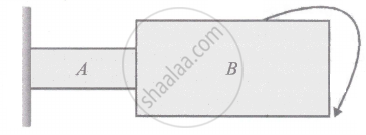
Two cylinders A and B of the same material have same length, their radii being in the ratio 1 : 2 respectively. The two are joined end to end as shown in the figure. One end of cylinder A is rigidly clamped while free end of cylinder B is twisted through an angle θ. The angle of twist of cylinder A is ______.
The initial pressure and volume of a gas enclosed in a cylinder are 2 × 105 N/m2 and 6 × 10-3 m3 respectively. If the work done in compressing the gas at constant pressure is 150 J. find the final volume of the gas.
A circular coil having N turns and radius r carries a current I. It is held in the XZ plane in a magnetic field `Bhati`. The torque on the coil due to the magnetic field is ______.
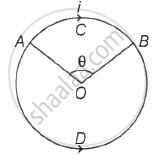
Equal current i flows in two segments of a circular loop in the direction shown in figure. Radius of the loop is r. The magnitude of magnetic field induction at the centre of the loop is ______.
An electron moving along positive X axis with a velocity of 8 ×107ms-1 enters a region having uniform magnetic field B = 1.3 × 10-3 T along positive Y axis.
- Explain why the electron describes a circular path.
- Calculate the radius of the circular path described by the electron.
