Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
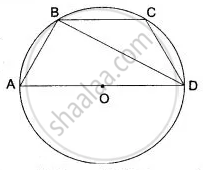
Prove that the rhombus, inscribed in a circle, is a square.
Solution
Let ABCD be a rhombus, inscribed in a circle
Now, ∠BAD + ∠BCD
(Opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal)
And ∠BAD + ∠BCD =180°
(Pair of opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary)
∴ ∠BAD + ∠BCD = `(180^circ)/2` = 90°
The other two angles are 90° and all the sides are equal.
∴ ABCD is a square.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the given figure, ∠BAD = 65°, ∠ABD = 70°, ∠BDC = 45°
1) Prove that AC is a diameter of the circle.
2) Find ∠ACB
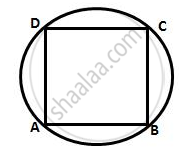
Prove that the parallelogram, inscribed in a circle, is a rectangle.
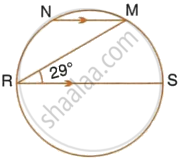
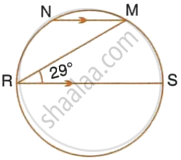
In the given figure, RS is a diameter of the circle. NM is parallel to RS and ∠MRS = 29°. Calculate : ∠RNM
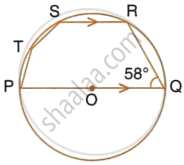
In the given figure, PQ is a diameter. Chord SR is parallel to PQ. Given that ∠PQR = 58°,
Calculate:
- ∠RPQ,
- ∠STP.
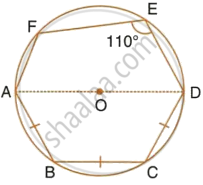
In the following figure, AD is the diameter of the circle with centre O. Chords AB, BC and CD are equal. If ∠DEF = 110°, calculate: ∠AEF
In the figure, given below, AB and CD are two parallel chords and O is the centre. If the radius of the circle is 15 cm, fins the distance MN between the two chords of lengths 24 cm and 18 cm respectively.

In the given figure, RS is a diameter of the circle. NM is parallel to RS and ∠MRS = 29°. Calculate : ∠NRM
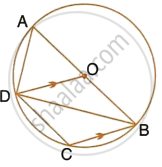
In the given figure, AB is a diameter of the circle with centre O. DO is parallel to CB and ∠DCB = 120°.
Calculate : ∠ADC
Also, show that the ΔAOD is an equilateral triangle.
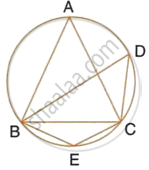
In the figure, ∠DBC = 58°. BD is diameter of the circle.
Calculate:
- ∠BDC
- ∠BEC
- ∠BAC
In the figure given alongside, AD is the diameter of the circle. If ∠ BCD = 130°, Calculate: (i) ∠ DAB (ii) ∠ ADB.