Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Show that the logarithmic function f : R0+ → R given by f (x) loga x ,a> 0 is a bijection.
Solution
`f R^+ → R given by f (x) = log_a x , a > 0`
Injectivity:
Let x and y be any two elements in the domain (N), such that f(x) = f(y).
f(x) = f(y)
`log_a x + log _a y`
⇒ x = y
So, f is one-one.
Surjectivity:
Let y be any element in the co-domain (R), such that f(x) = y for some element x in R+(domain).
f(x) = y
`log_a x = y`
⇒ `x = a^y in R^+`
So, for every element in the co-domain, there exists some pre-image in the domain.
⇒ f is onto.
Since f is one-one and onto, it is a bijection.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: N → N given by f(x) = x3
Show that the function f: R → R given by f(x) = x3 is injective.
Give an example of a function which is one-one but not onto ?
Prove that the function f : N → N, defined by f(x) = x2 + x + 1, is one-one but not onto
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 5x3 + 4
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 1 + x2
If A = {1, 2, 3}, show that a onto function f : A → A must be one-one.
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = x2 + 8 and g(x) = 3x3 + 1 .
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = x2 + 2x − 3 and g(x) = 3x − 4 .
Give examples of two functions f : N → Z and g : Z → Z, such that gof is injective but gis not injective.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = ex g(x) = loge x .
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = x2 g(x) = cos x .
If f(x) = |x|, prove that fof = f.
if `f (x) = sqrt(1-x)` and g(x) = `log_e` x are two real functions, then describe functions fog and gof.
Let f be a real function given by f (x)=`sqrt (x-2)`
Find each of the following:
(i) fof
(ii) fofof
(iii) (fofof) (38)
(iv) f2
Also, show that fof ≠ `f^2` .
Let
f (x) =`{ (1 + x, 0≤ x ≤ 2) , (3 -x , 2 < x ≤ 3):}`
Find fof.
If f : A → A, g : A → A are two bijections, then prove that fog is an injection ?
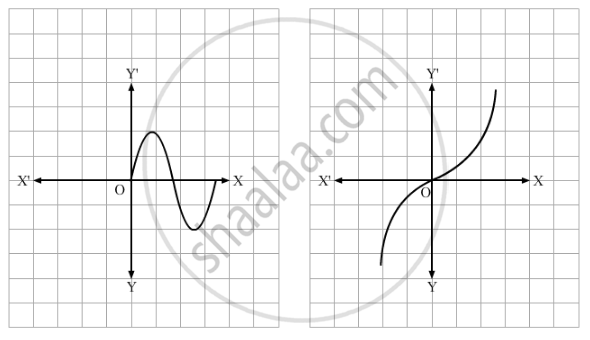
Which of the following graphs represents a one-one function?
If f : R → R is given by f(x) = x3, write f−1 (1).
If f : R → R defined by f(x) = 3x − 4 is invertible, then write f−1 (x).
Let \[f : \left[ - \frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2} \right] \to\] A be defined by f(x) = sin x. If f is a bijection, write set A.
Let f : R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 4x − 3 for all x ∈ R Then write f . [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
The range of the function
\[f\left( x \right) =^{7 - x} P_{x - 3}\]
If the function\[f : R \to \text{A given by} f\left( x \right) = \frac{x^2}{x^2 + 1}\] is a surjection, then A =
If \[f : R \to \left( - 1, 1 \right)\] is defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{- x|x|}{1 + x^2}, \text{ then } f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\] equals
Let \[f\left(x\right) = x^3\] be a function with domain {0, 1, 2, 3}. Then domain of \[f^{-1}\] is ______.
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let f : R→ R be defined as, f(x) = \[\begin{cases}2x, if x > 3 \\ x^2 , if 1 < x \leq 3 \\ 3x, if x \leq 1\end{cases}\]
Then, find f( \[-\]1) + f(2) + f(4)
The domain of the function f: R → R defined by f(x) = `sqrt(x^2 - 3x + 2)` is ______
Let A = [–1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions defined on A are one-one, onto or bijective:
k(x) = x2
The number of bijective functions from set A to itself when A contains 106 elements is ____________.
Range of `"f"("x") = sqrt((1 - "cos x") sqrt ((1 - "cos x")sqrt ((1 - "cos x")....infty))`
The function f: R → R defined as f(x) = x3 is:
A function f: x → y is said to be one – one (or injective) if:
'If 'f' is a linear function satisfying f[x + f(x)] = x + f(x), then f(5) can be equal to:
Prove that the function f is surjective, where f: N → N such that `f(n) = {{:((n + 1)/2",", if "n is odd"),(n/2",", if "n is even"):}` Is the function injective? Justify your answer.
The domain of the function `cos^-1((2sin^-1(1/(4x^2-1)))/π)` is ______.
Number of integral values of x satisfying the inequality `(3/4)^(6x + 10 - x^2) < 27/64` is ______.
Let f(x) be a polynomial of degree 3 such that f(k) = `-2/k` for k = 2, 3, 4, 5. Then the value of 52 – 10f(10) is equal to ______.
Let A = R – {2} and B = R – {1}. If f: A `→` B is a function defined by f(x) = `(x - 1)/(x - 2)` then show that f is a one-one and an onto function.
