Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If f(x) = |x|, prove that fof = f.
Solution
If f(x) = |x|, prove that fof = f.
(fof) (x) = f (f (x)) = f (|x|) = | |x| | = |x| = f (x)
So,
(fof) (x) = f (x), ∀x ∈ R
Hence, fof = f
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Prove that the greatest integer function f: R → R, given by f(x) = [x], is neither one-one nor onto, where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x.
Show that the function f: R → R given by f(x) = x3 is injective.
Give an example of a function which is neither one-one nor onto ?
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : Z → Z given by f(x) = x2
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Q → Q, defined by f(x) = x3 + 1
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 3 − 4x
Show that the logarithmic function f : R0+ → R given by f (x) loga x ,a> 0 is a bijection.
Suppose f1 and f2 are non-zero one-one functions from R to R. Is `f_1 / f^2` necessarily one - one? Justify your answer. Here,`f_1/f_2 : R → R is given by (f_1/f_2) (x) = (f_1(x))/(f_2 (x)) for all x in R .`
Give examples of two functions f : N → Z and g : Z → Z, such that gof is injective but gis not injective.
Find fog and gof if : f(x) = `x^2` + 2 , g (x) = 1 − `1/ (1-x)`.
Find f −1 if it exists : f : A → B, where A = {0, −1, −3, 2}; B = {−9, −3, 0, 6} and f(x) = 3 x.
If f : C → C is defined by f(x) = x2, write f−1 (−4). Here, C denotes the set of all complex numbers.
If f : R → R defined by f(x) = 3x − 4 is invertible, then write f−1 (x).
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. State whether f is one-one or not.
Let
\[f : R \to R\] be a function defined by
Let
Let
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : x \geq 1 \right\}\] The inverse of the function,
\[f : A \to A\] given by
\[f\left( x \right) = 2^{x \left( x - 1 \right)} , is\]
Let
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : x \leq 1 \right\} and f : A \to A\] be defined as
\[f\left( x \right) = x \left( 2 - x \right)\] Then,
\[f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\] is
If the function
\[f : R \to R\] be such that
\[f\left( x \right) = x - \left[ x \right]\] where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x, then \[f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\]
Let \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{\alpha x}{x + 1}, x \neq - 1\] Then, for what value of α is \[f \left( f\left( x \right) \right) = x?\]
If \[f\left( x \right) = \sin^2 x\] and the composite function \[g\left( f\left( x \right) \right) = \left| \sin x \right|\] then g(x) is equal to
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let f : R → R be given by f(x) = tanx. Then, f-1(1) is
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let A = {1, 2, ... , n} and B = {a, b}. Then the number of subjections from A into B is
Write about strlen() function.
Let f: R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 4x – 3 ∀ x ∈ R. Then write f–1
Set A has 3 elements and the set B has 4 elements. Then the number of injective mappings that can be defined from A to B is ______.
The domain of the function f: R → R defined by f(x) = `sqrt(x^2 - 3x + 2)` is ______
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
h = {(1,4), (2, 5), (3, 5)}
Let A = {1, 2, 3, ...n} and B = {a, b}. Then the number of surjections from A into B is ______.
If f(x) = (4 – (x – 7)3}, then f–1(x) = ______.
A general election of Lok Sabha is a gigantic exercise. About 911 million people were eligible to vote and voter turnout was about 67%, the highest ever

Let I be the set of all citizens of India who were eligible to exercise their voting right in the general election held in 2019. A relation ‘R’ is defined on I as follows:
R = {(V1, V2) ∶ V1, V2 ∈ I and both use their voting right in the general election - 2019}
- Three friends F1, F2, and F3 exercised their voting right in general election-2019, then which of the following is true?
An organization conducted a bike race under 2 different categories-boys and girls. Totally there were 250 participants. Among all of them finally, three from Category 1 and two from Category 2 were selected for the final race. Ravi forms two sets B and G with these participants for his college project. Let B = {b1,b2,b3} G={g1,g2} where B represents the set of boys selected and G the set of girls who were selected for the final race.
Ravi decides to explore these sets for various types of relations and functions.
- Let R: B → G be defined by R = { (b1,g1), (b2,g2),(b3,g1)}, then R is ____________.
An organization conducted a bike race under 2 different categories-boys and girls. Totally there were 250 participants. Among all of them finally, three from Category 1 and two from Category 2 were selected for the final race. Ravi forms two sets B and G with these participants for his college project. Let B = {b1,b2,b3} G={g1,g2} where B represents the set of boys selected and G the set of girls who were selected for the final race.
Ravi decides to explore these sets for various types of relations and functions.
- Ravi wants to find the number of injective functions from B to G. How many numbers of injective functions are possible?
Raji visited the Exhibition along with her family. The Exhibition had a huge swing, which attracted many children. Raji found that the swing traced the path of a Parabola as given by y = x2.
Answer the following questions using the above information.
- Let f: {1,2,3,....} → {1,4,9,....} be defined by f(x) = x2 is ____________.
If `f : R -> R^+ U {0}` be defined by `f(x) = x^2, x ∈ R`. The mapping is
Prove that the function f is surjective, where f: N → N such that `f(n) = {{:((n + 1)/2",", if "n is odd"),(n/2",", if "n is even"):}` Is the function injective? Justify your answer.
Find the domain of sin–1 (x2 – 4).
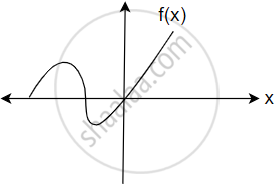
The given function f : R → R is not ‘onto’ function. Give reason.
