Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The internal energy of an ideal gas decreases by the same amount as the work done by the system.
(a) The process must be adiabatic.
b) The process must be isothermal.
(c) The process must be isobaric.
(d) The temperature must decrease.
Solution
(a) The process must be adiabatic
(d) The temperature must decrease.
Using the first law of thermodynamics, we get
\[\Delta Q = \Delta W + \Delta U\]
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta Q = 0 .........\left[ \because \Delta W = - \Delta U \right]\]
Thus, no heat is exchanged in the process, i.e. the process is adiabatic and since the internal energy is decreasing, the temperature must decrease because the gas is an ideal gas.
On the other hand, volume and pressure of the gas are varying, leading to positive work done. So, the process cannot be isochoric and isobaric.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics for Isothermal Process
Calculate the change in internal energy of a gas kept in a rigid container when 100 J of heat is supplied to it.
A gas is enclosed in a cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston. The gas is slowly heated for some time. During the process, 10 J of heat is supplied and the piston is found to move out 10 cm. Find the increase in the internal energy of the gas. The area of cross section of the cylinder = 4 cm2 and the atmospheric pressure = 100 kPa.
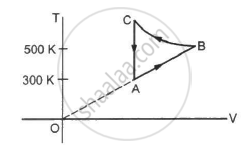
Consider the cyclic process ABCA, shown in figure, performed on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas. A total of 1200 J of heat is withdrawn from the sample in the process. Find the work done by the gas during the part BC.
A solar cooker and a pressure cooker both are used to cook food. Treating them as thermodynamic systems, discuss the similarities and differences between them.
Based on first law of thermodynamics which of the following is correct.
Calculate the amount of work done during isothermal expansion of a gas from a volume of 4 dm3 to 6 dm3 against a constant external pressure of 3 atmosphere?
Change in internal energy, when 4 KJ of work is done on the system and 1 KJ heat is given out by the system, is:
An ideal gas undergoes cyclic process ABCDA as shown in given P-V diagram (figure). The amount of work done by the gas is ______.

Can a system be heated and its temperature remains constant?
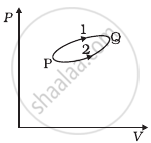
A system goes from P to Q by two different paths in the P-V diagram as shown in figure. Heat given to the system in path 1 is 1000 J. The work done by the system along path 1 is more than path 2 by 100 J. What is the heat exchanged by the system in path 2?
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure.
A to B : volume constant
B to C : adiabatic
C to D : volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
VC = VD = 2VA = 2VB
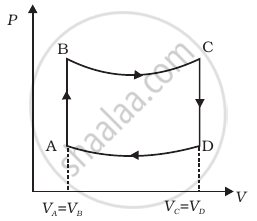
- In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
- In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
- What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA.
- What is the efficiency of the engine?
(γ = `5/3` for the gas), (Cv = `3/2` R for one mole)
The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 4 moles of a rigid diatomic gas from 0°C to 50°C when no work is done is ______.
(R is the universal gas constant.)
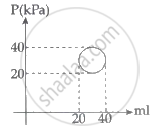
In the reported figure, heat energy absorbed by a system in going through a cyclic process is ______ πJ.
If one mole of monoatomic gas `(gamma=5/3)` is mixed with one mole of diatomic gas `(gamma=7/5)`, the value of γ for the mixture is ______.
What is true for an adiabatic process?
Using the first law of thermodynamics, show that for an ideal gas, the difference between the molar specific heat capacities at constant pressure and at constant volume is equal to the molar gas constant R.
Show that the heat absorbed at constant pressure is equal to the change in enthalpy of the system.
Define isochoric process
What is an isothermal process?
