Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Through the mid-point M of the side CD of a parallelogram ABCD, the line BM is drawn intersecting diagonal AC in L and AD produced in E. Prove that: EL = 2BL.
Solution
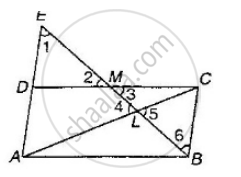
∠1 = ∠6 (Alternate interior angles)
∠2 = ∠3 (Vertically opposite angles)
DM = MC (M is the mid-point of CD)
ΔDEM ≅ ΔCBM (AAS Congruence criterion)
So, DE = BC (Corresponding parts of congruent triangles)
Also, AD = BC (Opposite sides of a parallelogram)
AE = AD + DE = 2BC
Now, ∠1 = ∠6 and ∠4 = ∠5
ΔELA ∼ ΔBLC (AA similarity)
`=> (EL)/(BL) = (EA)/(BC)`
`=> (EL)/(BL) = (2BC)/(BC) = 2`
`=>` EL = 2BL
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
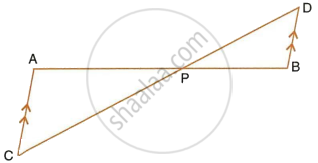
In the figure, given below, straight lines AB and CD intersect at P; and AC || BD. Prove that: ΔAPC and ΔBPD are similar.
P is a point on side BC of a parallelogram ABCD. If DP produced meets AB produced at point L, prove that: DL : DP = AL : DC.
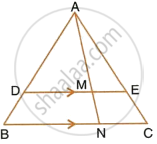
In the given figure, DE || BC, AE = 15 cm, EC = 9 cm, NC = 6 cm and BN = 24 cm.
- Write all possible pairs of similar triangles.
- Find lengths of ME and DM.
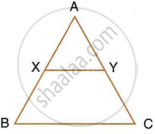
In the following figure, XY is parallel to BC, AX = 9 cm, XB = 4.5 cm and BC = 18 cm.

Find : `(YC)/(AC)`
In the following figure, ∠AXY = ∠AYX. If `(BX)/(AX) = (CY)/(AY)`, show that triangle ABC is isosceles.
In the given figure, AB and DE are perpendiculars to BC.
Find the ratio of the area of a ΔABC : area of ΔDEC.

Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
If area (ΔABC) = 16 cm, area (ΔDEF) = 25 cm2 and BC = 2.3 cm find EF.
In the adjoining figure ABC is a right angle triangle with ∠BAC = 90°, and AD ⊥ BC.
(i) Prove ΔADB ∼ ΔCDA.
(ii) If BD = 18 cm, CD = 8 cm find AD.
(iii) Find the ratio of the area of ΔADB is to area of ΔCDA.
In the given figure ΔABC and ΔAMP are right angled at B and M respectively.
Given AC = 10 cm, AP = 15 cm and PM = 12 cm.
(i) Prove ΔABC ∼ Δ AMP.
(ii) Find AB and BC.
Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
If area (ΔABC) = 9 cm2, area (ΔDEF) = 64 cm2 and BC = 5·1 cm find AB.
