Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
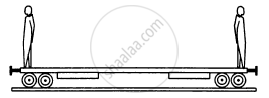
Two persons each of mass m are standing at the two extremes of a railroad car of mass M resting on a smooth track(In the following figure). The person on left jumps to the left with a horizontal speed u with respect to the state of the car before the jump. Thereafter, the other person jumps to the right, again with the same horizontal speed u with respect to the state of the car before his jump. Find the velocity of the car after both the persons have jumped off.
Solution
It is given that:
Mass of each persons = m
Mass of railroad car = M
Let the velocity of the railroad w.r.t. earth, when the man on the left jumps off be V.
By the law of conservation of momentum:
\[0 = - mu + (M + m)V\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = \left( \frac{mu}{M + m} \right), \text{ towards right }\]
When the man on the right jumps, his velocity w.r.t. the car is u.
\[0 = mu - MV'\]
\[ \Rightarrow V' = \frac{mu}{M}\]
(V is the change in velocity of the platform when the platform itself is taken as reference, assuming the car to be at rest.)
∴ Net velocity towards left, (i.e. the velocity of the car)
\[V' - V = \frac{mu}{M} - \frac{mu}{(M + m)}\]
\[ = \frac{mMu + m^2 u - Mmu}{M(M + m)}\]
\[ \Rightarrow V' - V = \frac{m^2 u}{M(M + m)}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The centre of mass is defined as \[\vec{R} = \frac{1}{M} \sum_i m_i \vec{r_i}\]. Suppose we define "centre of charge" as \[\vec{R}_c = \frac{1}{Q} \sum_i q_i \vec{r_i}\] where qi represents the ith charge placed at \[\vec{r}_i\] and Q is the total charge of the system.
(a) Can the centre of charge of a two-charge system be outside the line segment joining the charges?
(b) If all the charges of a system are in X-Y plane, is it necessary that the centre of charge be in X-Y plane?
(c) If all the charges of a system lie in a cube, is it necessary that the centre of charge be in the cube?
You are waiting for a train on a railway platform. Your three-year-old niece is standing on your iron trunk containing the luggage. Why does the trunk not recoil as she jumps off on the platform?
You are holding a cage containing a bird. Do you have to make less effort if the bird flies from its position in the cage and manages to stay in the middle without touching the walls of the cage? Does it makes a difference whether the cage is completely closed or it has rods to let air pass?
Consider the following two statements:
(A) Linear momentum of the system remains constant.
(B) Centre of mass of the system remains at rest.
Consider a system of two identical particles. One of the particles is at rest and the other has an acceleration a. The centre of mass has an Acceleration
Two blocks of masses 10 kg and 30 kg are placed along a vertical line. The first block is raised through a height of 7 cm. By what distance should the second mass be moved to raise the centre of mass by 1 cm?
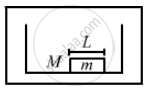
Consider a gravity-free hall in which a tray of mass M, carrying a cubical block of ice of mass m and edge L, is at rest in the middle. If the ice melts, by what distance does the centre of mass of "the tray plus the ice" system descend?
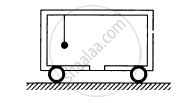
A car of mass M is at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface and a pendulum bob of mass m hangs from the roof of the cart. The string breaks, the bob falls on the floor, makes serval collisions on the floor and finally lands up in a small slot made in the floor. The horizontal distance between the string and the slot is L. Find the displacement of the cart during this process.
A particle of mass 100 g moving at an initial speed u collides with another particle of same mass kept initially at rest. If the total kinetic energy becomes 0.2 J after the collision, what could be the minimum and the maximum value of u.
A projectile is fired with a speed u at an angle θ above a horizontal field. The coefficient of restitution of collision between the projectile and the field is e. How far from the starting point, does the projectile makes its second collision with the field?
A block of mass m is placed on a triangular block of mass M which in turn is placed on a horizontal surface as shown in figure. Assuming frictionless surfaces find the velocity of the triangular block when the smaller block reaches the bottom end.
Two small balls A and B, each of mass m, are joined rigidly to the ends of a light rod of length L (see the following figure). The system translates on a frictionless horizontal surface with a velocity \[\nu_0\] in a direction perpendicular to the rod. A particle P of mass m kept at rest on the surface sticks to the ball A as the ball collides with it. Find
(a) the linear speeds of the balls A and B after the collision, (b) the velocity of the centre of mass C of the system A + B + P and (c) the angular speed of the system about C after the collision.
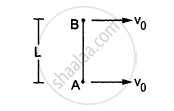
[Hint : The light rod will exert a force on the ball B
only along its length.]
Solve the following problem.
A uniform solid sphere of radius R has a hole of radius R/2 drilled inside it. One end of the hole is at the center of the sphere while the other is at the boundary. Locate center of mass of the remaining sphere.
Find out the centre of mass for the given geometrical structures.
a) Equilateral triangle
b) Cylinder
c) Square
Two particles P and Q of mass 1 kg and 3 kg respectively start moving towards each other from rest under mutual attraction. What is the velocity of their center of mass?
In system of two particles of masses 'm1' and 'm2', the first particle is moved by a distance 'd' towards the centre of mass. To keep the centre of mass unchanged, the second particle will have to be moved by a distance ______.
A bullet of mass 20 gram is fired from a gun of mass 2.5 kg with a speed of 750 m/s. The magnitude of recoil velocity of the gun is ______.
For which of the following does the centre of mass lie outside the body?
The density of a non-uniform rod of length 1 m is given by ρ(x) = a(1 + bx2) where a and b are constants and 0 ≤ x ≤ 1. The centre of mass of the rod will be at ______.
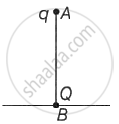
A point charge Q is situated at point B on the ground. A point charge q of mass m is vertically dropped along line AB from a multi-storey building of height h. Find the position of the point charge q when it is in equilibrium.