Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide
alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide.
Solution
\[\ce{\underset{\text{ethylbromide}}{C2H5Br} + alc KOH ->\underset{\text{ethene}}{CH2} = CH2 + KBr + H2O}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which would undergo SN1 reaction faster in the following pair and why?
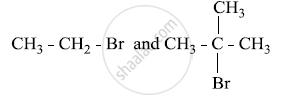
What are ambident nucleophiles? Explain with an example.
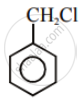
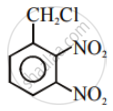
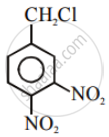
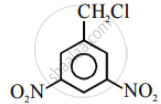
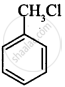
Out of C6H5CH2Cl and C6H5CHClC6H5, which is more easily hydrolysed by aqueous KOH.
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide:
moist silver oxide
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide?
moist silver oxide
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide:
silver acetate
In a coordination entity of the type [PtCl2(en)2]2+ which isomer will show optical isomerism?
In the reaction, \[\ce{R - X + NaOR' -> ROR’ + X}\] ( – ve ion). The main product formed is:
Arrange the following organic compounds in descending order of their reactivity towards SN1 reaction.
C6H5CH2Br, C6H5CH(C6H5)Br, C6H5CH(CH3)Br, C6H5C(CH3)(C6H5)Br
Which of the following is optically inactive?
Optically active isomers but not mirror images are called ____________.
Which of the following is an optically active compound?
Which of the following compounds is optically active?
SN1 reaction of alkyl halides lead to ___________.
Identify the end product (C) in the following sequence:
\[\ce{C2H5OH ->[SOCl2][Pyridine] A ->[KCN {(alc.)}] B ->[2H2O/H^+] C}\]
Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism?
The increasing order of nucleophilicity would be:
Which of the following compound will undergo racemisation when reacts with aq. KOH?
(i)
(ii)
CH3CH2CH2Cl
(iii)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2Cl}
\end{array}\]
(iv)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\ce{CH3-C-Cl}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{C2H5}
\end{array}\]
The increasing order of reactivity towards SN1 mechanism is:
(I) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2-CH3}\\
|\phantom{........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
(II) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(III) P–CH3O–C6H4–CH2Cl
A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo ______.
Which one is the correct order of nucleophilic strength (pKa) of following nucleophiles?
When CH3CH2CHCl2 is treated NaNH2 product formed is:-
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
The decreasing order of reactivity of the following compounds towards nucleophilic substitution (SN2) is ______.
Inversion of configuration occurs in ______.
Complete the reaction with the main product formed:

Identify the product in the following reaction: 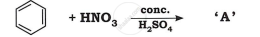
Discuss SN2 mechanism of methyl bromide using aqueous KOH.
Which alkyl halide from the following pair would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism? Explain your answer.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3CH2CHCH3}\\\phantom{...}|\\\phantom{....}\ce{Br}\end{array}\] or \[\begin{array}{cc}\phantom{.....}\ce{CH3}\\\phantom{..}|\\\ce{H3C - C - Br}\\\phantom{..}|\\\phantom{....}\ce{CH3}\end{array}\]