Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide:
silver acetate
Write the chemical reaction for the following:
Ethyl bromide is heated with silver acetate.
Solution
\[\ce{\underset{\text{ethyl bromide}}{C2H5Br} +\underset{\text{silver acetate}}{CH3COOAg}->CH3COOC2H5 + AgBr}\]
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the structure of an isomer of compound C4H9Br which is most reactive towards SN1 reaction
Given reasons: C–Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than C–Cl bond length in CH3–Cl.
Which compound in the following pair will react faster in SN2 reaction with OH−?
CH3Br or CH3I
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Toluene to benzyl alcohol
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH(Br)CH2CH3 + NaOH ->[water]}\]
Out of C6H5CH2Cl and C6H5CHClC6H5, which is more easily hydrolysed by aqueous KOH.
What happens when ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH?
What happens when methyl chloride is treated with KCN?
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide:
moist silver oxide
In the reaction, \[\ce{R - X + NaOR' -> ROR’ + X}\] ( – ve ion). The main product formed is:
Which of the following is optically inactive?
Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched?
| Reaction | Product | |
| I | RX + AgCN | RNC |
| II | RX + KCN | RCN |
| III | RX + KNO2 | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{.......}\ce{O}\\ \phantom{.....}/\\ \ce{R - N}\phantom{....}\\ \phantom{.....}\backslash\backslash\\ \phantom{.......}\ce{O} \end{array}\] |
| IV | RX + AgNO2 | \[\ce{R-O-N=O}\] |
The order of reactivities of the following alkyl halides for an SN2 reaction is:
Which of the following is the correct order of decreasing SN2 reactivity?
2-Bromopentane is heated with potassium ethoxide in ethanol. The major product obtained is ____________.
Which of the following is a chiral compound?
SN1 reaction of alkyl halides lead to ___________.
Identify the end product (C) in the following sequence:
\[\ce{C2H5OH ->[SOCl2][Pyridine] A ->[KCN {(alc.)}] B ->[2H2O/H^+] C}\]
The increasing order of nucleophilicity would be:
Which of the following compound will undergo racemisation when reacts with aq. KOH?
(i)
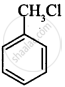
(ii)
CH3CH2CH2Cl
(iii)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2Cl}
\end{array}\]
(iv)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\ce{CH3-C-Cl}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{C2H5}
\end{array}\]
The increasing order of reactivity towards SN1 mechanism is:
(I) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2-CH3}\\
|\phantom{........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
(II) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(III) P–CH3O–C6H4–CH2Cl
Which of the following alkyl halides will undergo SN1 reaction most readily?
Assertion: KCN reacts with methyl chloride to give methyl isocyanide.
Reason: CN– is an ambident nucleophile.
A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo ______.
Cyanide ion acts as an ambident nucleophile. From which end it acts as a stronger nucleophile in aqueous medium? Give reason for your answer.
Give reason for the following:
The product formed during SN1 reaction is a racemic mixture.
In which reaction mechanism carbocation is formed?
Assertion (A) : Nucleophilic substitution of iodoethane is easier than chloroethane.
Reason (R) : Bond enthalpy of C-I bond is less than that of C-Cl bond.
An organic compound A with the molecular formula (+) C4H9Br undergoes hydrolysis to form (+) C4H9OH. Give the structure of A and write the mechanism of the reaction.
