Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide:
moist silver oxide
Solution
\[\ce{2C2H5Br + Ag2O->C2H5 - O - C2H5 + 2AgBr}\]
\[\ce{Ag2O + H2O -> 2AgOH}\]
\[\ce{AgOH + C2H5Br -> C2\underset{\text{Ethanol}}{H5OH} + AgBr }\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of bromomethane.
Out of 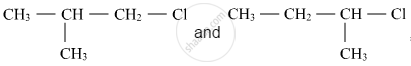 , which is more reactive towards SN1 reaction and why?
, which is more reactive towards SN1 reaction and why?
Given reasons: C–Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than C–Cl bond length in CH3–Cl.
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Toluene to benzyl alcohol
Arrange the compounds of the following set in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane
Arrange the compounds of the following set in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
1-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-3-methylbutane
What happens when ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH?
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Ethyl chloride to propanoic acid
Given reasons: The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
Identify 'A' in the following reaction -
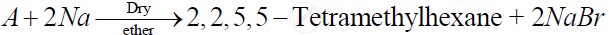
(a) 2- Bromo-2 methylbutane
(b) 1 -Bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane
(c) 1 - Bromo - 3 -methylbutane
(d) 1 - Bromo- 2 -methylpropane
Which would undergo SN2 reaction faster in the following pair and why ?
CH3 – CH2 – Br and CH3 – CH2 – I
In the reaction, \[\ce{R - X + NaOR' -> ROR’ + X}\] ( – ve ion). The main product formed is:
Which of the following reactions is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction?
The order of reactivity of the given haloalkanes towards nucleophile is:
Tertiary alkyl halides are practically inert to substitution by SN2 mechanism because of ____________.
An important chemical method to resolve a racemic mixture makes use of the formation of ______.
2-Bromopentane is heated with potassium ethoxide in ethanol. The major product obtained is ____________.
Among the following, the dissociation constant is highest for:
The correct order of increasing the reactivity of C–X bond towards nucleophile in following compounds.
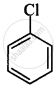
(I)
(II)
(CH3)3CCl
(III)
(CH3)2CHCl
(IV)
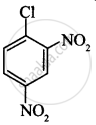
Write the structures and names of the compounds formed when compound ‘A’ with molecular formula, \[\ce{C7H8}\] is treated with \[\ce{Cl2}\] in the presence of \[\ce{FeCl3}\].
Elimination reactions (especially β-elimination) are as common as the nucleophilic substitution reaction in case of alkyl halides. Specify the reagents used in both cases.
Cyanide ion acts as an ambident nucleophile. From which end it acts as a stronger nucleophile in aqueous medium? Give reason for your answer.
Which of the following is the definition of chirality?
Which one is the correct order of nucleophilic strength (pKa) of following nucleophiles?
Give reason for the following:
The product formed during SN1 reaction is a racemic mixture.
The number of chiral alcohol (s) with molecular formula C4H10O is ______.
Assertion (A) : Nucleophilic substitution of iodoethane is easier than chloroethane.
Reason (R) : Bond enthalpy of C-I bond is less than that of C-Cl bond.
Retention of configuration is observed in ______.
Give the mechanism of the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2OH ->[H2SO4][413 K] CH3CH2-O-CH2CH3 + H2O}\]
