Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the following statement is correct?
Options
Opposite angles of a parallelogram are not equal.
Adjacent angles of a parallelogram are complementary.
Diagonals of a parallelogram are always equal.
Both pairs of opposite sides of a parallelogram are always equal.
Solution
Both pairs of opposite sides of a parallelogram are always equal.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
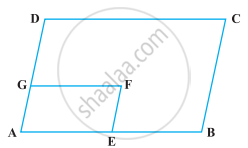
The alongside figure shows a parallelogram ABCD in which AE = EF = FC.
Prove that:
- DE is parallel to FB
- DE = FB
- DEBF is a parallelogram.
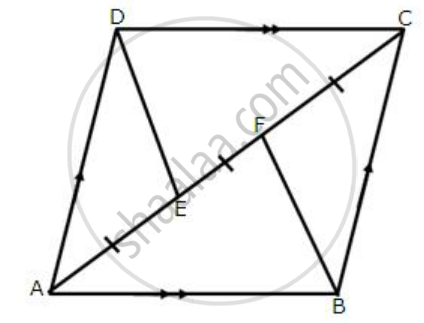
In the alongside diagram, ABCD is a parallelogram in which AP bisects angle A and BQ bisects angle B.

Prove that:
- AQ = BP
- PQ = CD
- ABPQ is a parallelogram.
Prove that the bisectors of opposite angles of a parallelogram are parallel.
In parallelogram ABCD, the bisector of angle A meets DC at P and AB = 2 AD.
Prove that:
(i) BP bisects angle B.
(ii) Angle APB = 90o.
PQRS is a parallelogram. T is the mid-point of PQ and ST bisects ∠PSR.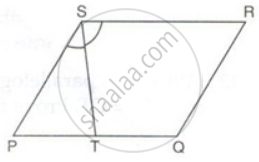
Prove that: RT bisects angle R
ABCD is a parallelogram. The bisector of ∠BAD meets DC at P, and AD is half of AB.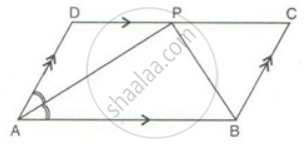
Prove that: BP bisects ∠ABC.
In a parallelogram ABCD, E is the midpoint of AB and DE bisects angle D. Prove that:CE is the bisector of angle C and angle DEC is a right angle
In the given figure, the perimeter of parallelogram PQRS is 42 cm. Find the lengths of PQ and PS.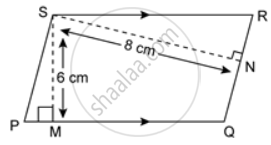
In parallelogram ABCD of the accompanying diagram, line DP is drawn bisecting BC at N and meeting AB (extended) at P. From vertex C, line CQ is drawn bisecting side AD at M and meeting AB (extended) at Q. Lines DP and CQ meet at O. Show that the area of triangle QPO is `9/8` of the area of the parallelogram ABCD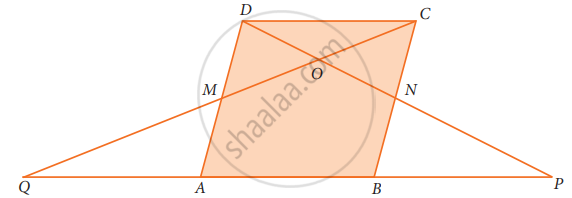
In the following figure, ABCD and AEFG are two parallelograms. If ∠C = 55º, determine ∠F.