Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Polynomials
3: Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
4: Quadratic Equations
5: Arithmetic Progressions
6: Triangles
7: Coordinate Geometry
8: Introduction to Trigonometry
9: Some Applications of Trigonometry
▶ 10: Circles
11: Constructions
12: Areas Related to Circles
13: Surface Areas and Volumes
14: Statistics
15: Probability
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 10: Circles
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 10 of CBSE, Karnataka Board NCERT for Mathematics [English] Class 10.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 10 Circles Exercise 10.1 [Page 209]
How many tangents can a circle have?
A tangent to a circle intersects it in ______ point (s).
A line intersecting a circle in two points is called a ______.
A circle can have ______ parallel tangents at the most.
The common point of a tangent to a circle and the circle is called ______.
A tangent PQ at a point P of a circle of radius 5 cm meets a line through the centre O at a point Q so that OQ = 12 cm. Length PQ is ______.
12 cm
13 cm
8.5 cm
`sqrt119` cm
Draw a circle and two lines parallel to a given line such that one is a tangent and the other, a secant to the circle.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 10 Circles Exercise 10.2 [Pages 213 - 214]
From a point Q, the length of the tangent to a circle is 24 cm and the distance of Q from the centre is 25 cm. The radius of the circle is ______.
7 cm
12 cm
15 cm
24.5 cm
In the given figure, if TP and TQ are the two tangents to a circle with centre O so that ∠POQ = 110°, then ∠PTQ is equal to ______.
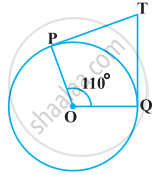
60°
70°
80°
90°
If tangents PA and PB from a point P to a circle with centre O are inclined to each other an angle of 80°, then ∠POA is equal to ______.
50°
60°
70°
80°
40°
Prove that the tangents drawn at the ends of a diameter of a circle are parallel.
Prove that the perpendicular at the point of contact to the tangent to a circle passes through the centre.
The length of a tangent from a point A at distance 5 cm from the centre of the circle is 4 cm. Find the radius of the circle.
Two concentric circles are of radii 5 cm and 3 cm. Find the length of the chord of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle.
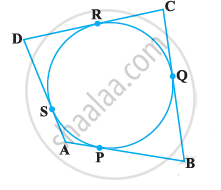
In the following Fig, a quadrilateral ABCD is drawn to circumscribe a circle, with centre O, in such a way that the sides AB, BC, CD and DA touch the circle at the points P, Q, R and S respectively. Prove that AB + CD = BC + DA.
In the given figure, XY and X’Y’ are two parallel tangents to a circle with centre O and another tangent AB with point of contact C intersecting XY at A and X’Y’ at B. Prove that ∠AOB = 90°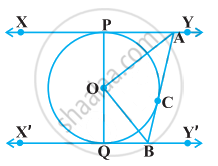
Prove that the angle between the two tangents drawn from an external point to a circle is supplementary to the angle subtended by the line segments joining the points of contact to the centre.
Prove that a parallelogram circumscribing a circle is a rhombus.
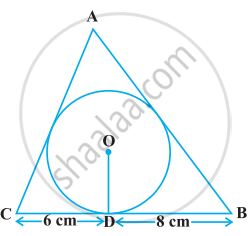
A triangle ABC is drawn to circumscribe a circle of radius 4 cm such that the segments BD and DC into which BC is divided by the point of contact D are of lengths 8 cm and 6 cm respectively (see given figure). Find the sides AB and AC.
Prove that opposite sides of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle subtend supplementary angles at the centre of the circle.
Solutions for 10: Circles
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 10 - Circles
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE, Karnataka Board Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 CBSE, Karnataka Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 CBSE, Karnataka Board 10 (Circles) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 10 Circles are Tangent to a Circle, Number of Tangents from a Point on a Circle, Concept of Circle, Tangent to a Circle, Number of Tangents from a Point on a Circle, Concept of Circle, Tangent to a Circle, Number of Tangents from a Point on a Circle, Concept of Circle.
Using NCERT Mathematics [English] Class 10 solutions Circles exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE, Karnataka Board Mathematics [English] Class 10 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 10, Circles Mathematics [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 CBSE, Karnataka Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
![NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 10 - Circles NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 10 - Circles - Shaalaa.com](/images/9788174506344-mathematics-english-class-10_6:608765d445324ac894a5bdfeb0e3a93a.jpg)
