Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A line intersecting a circle in two points is called a ______.
Solution
A line intersecting a circle in two points is called a secant.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the given circle with centre O, ∠ABC = 100°, ∠ACD = 40° and CT is a tangent to the circle at C. Find ∠ADC and ∠DCT.

Draw a circle of radius 3.5 cm. Marks a point P outside the circle at a distance of 6 cm from the centre. Construct two tangents from P to the given circle. Measure and write down the length of one tangent.
In Figure 5, a triangle PQR is drawn to circumscribe a circle of radius 6 cm such that the segments QT and TR into which QR is divided by the point of contact T, are of lengths 12 cm and 9 cm respectively. If the area of ΔPQR = 189 cm2, then find the lengths of sides PQ and PR.
Prove that a diameter AB of a circle bisects all those chords which are parallel to the tangent at the point A.
In following fig., PT is a tangent to the circle at T and PAB is a secant to the same circle. If PA = 4cm and AB = Scm, find PT.
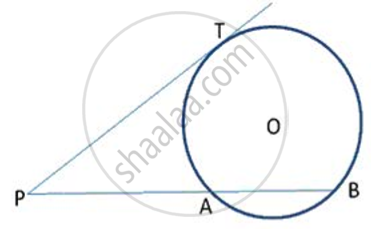
The length of the direct common tangent to two circles of radii 12cm and 4cm is 15cm. calculate the distance between their centres.
Calculate the length of direct common tangent to two circles of radii 3cm and Bern with their centres 13cm apart.
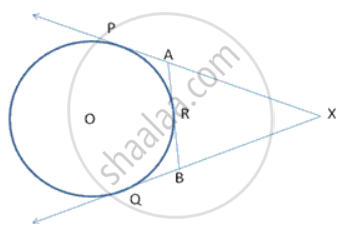
In the figure, XP and XQ are tangents from X to the circle with centre O. R is a point on the circle. Prove that XA + AR = XB + BR.
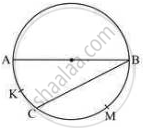
In the following figure, seg AB is a diameter of the circle, m (arc AKC) = 40°. Find the value of m (arc BMC).
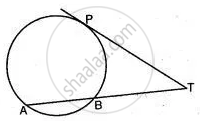
In the figure given below, PT is a tangent to the circle. Find PT if AT = 16 cm and AB = 12 cm.
Draw a circle of radius 2.7 cm and draw a chord PQ of length 4.5 cm. Draw tangents at points P and Q without using centre.
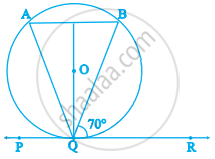
In figure, if PQR is the tangent to a circle at Q whose centre is O, AB is a chord parallel to PR and ∠BQR = 70°, then ∠AQB is equal to ______.
In the figure, PQ and PR are tangents to a circle with centre A. If ∠QPA=27°, then ∠QAR equals to ______
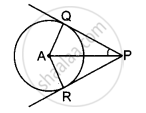
Prove that the tangents drawn at the ends of a chord of a circle make equal angles with the chord.
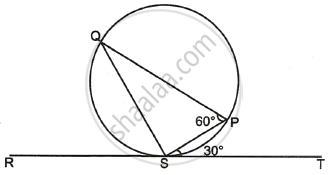
In the given figure, PA is a tangent to the circle drawn from the external point P and PBC is the secant to the circle with BC as diameter. If ∠AOC = 130°, then find the measure of ∠APB, where O is the centre of the circle.
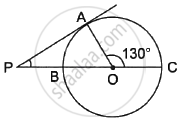
In the given diagram RT is a tangent touching the circle at S. If ∠PST = 30° and ∠SPQ = 60°, then ∠PSQ is equal to ______.
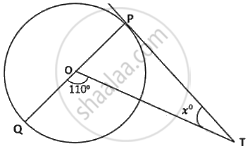
In the adjoining diagram, O is the centre of the circle and PT is a tangent. The value of x is ______.