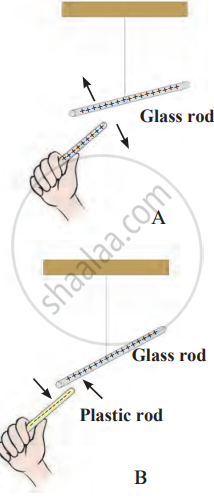
1. Aim: To observe how objects with similar and opposite electric charges behave.
2. Requirements: Two glass rods, silk cloth, a plastic rod, woollen cloth, and thread for suspending the rod.
3. Procedure
- Charging the glass rod: Rub one end of a glass rod with a silk cloth to charge it. Suspend the charged glass rod freely in the air using a thread.
- Testing with another glass rod: Rub another glass rod with a silk cloth to charge it. Bring it close to the suspended glass rod.
Observation: The two rods push each other away (repulsion). - Testing with a plastic rod: Rub one end of a plastic rod with a woollen cloth to charge it. Bring it near the suspended glass rod.
Observation: The rods attract each other (attraction).
4. Conclusion: Similar charges repel each other (like in the case of the two glass rods). Opposite charges attract each other (like the plastic rod and the glass rod). Benjamin Franklin named these charges as positive (+) and negative (-).