Topics
Roman Numerals
Number Work
Addition and Subtraction
Multiplication and Division
Fractions
Angles
Circles
Multiples and Factors
Decimal Fractions
- Decimal Fractions
- The Decimal Number System
- Concept of Tenths, Hundredths and Thousandths in Decimal
- Concept of Place Value
- Use of Decimal Fraction
- Writing Half, Quarter, Three-quarters and One and a Quarter in Decimal Form
- Addition of Decimal Fraction
- Subtraction of Decimal Fraction
- Decimals Used for Measurement
Measuring Time
Problems on Measurement
Perimeter and Area
Three Dimensional Objects and Nets
Pictographs
Patterns
Preparation for Algebra
Inequality
In mathematics, when two expressions do not have the same value, they are not equal. This is represented using the "≠" (not equal to) symbol.
For example:
(7 + 5) ≠ (7 × 5) since 12 ≠ 35
Such representations are called inequalities.
If two expressions are not equal, one must be greater or smaller than the other. To indicate this, we use the symbols “<” (less than) and “>” (greater than).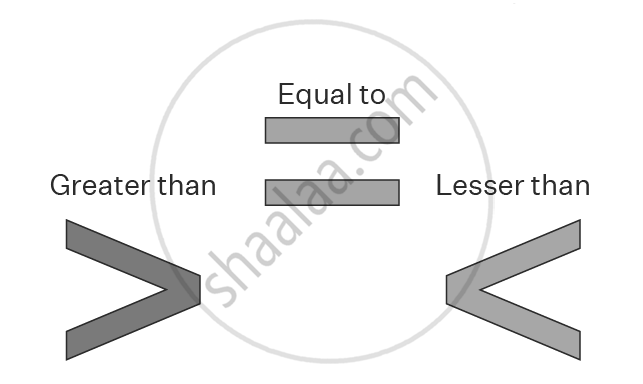
For example:
(9 − 5) = 4, (15 ÷ 3) = 5
Since 4 is less than 5, we write:
(9 − 5) < (15 ÷ 3) or (15 ÷ 3) > (9 − 5)
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
