Topics
Number System
Rational Numbers
- Rational Numbers
- Addition of Rational Number
- Subtraction of Rational Number
- Multiplication of Rational Numbers
- Division of Rational Numbers
- Rational Numbers on a Number Line
- Inserting Rational Numbers Between Two Given Rational Numbers
- Method of Finding a Large Number of Rational Numbers Between Two Given Rational Numbers
Exponents
- Concept of Exponents
- Law of Exponents (For Integral Powers)
- Negative Integral Exponents
- More About Exponents
Squares and Square Root
- Concept of Square Roots
- Finding Square Root by Division Method
- Finding Square Root Through Prime Factorisation
- To Find the Square Root of a Number Which is Not a Perfect Square (Using Division Method)
- Properties of Square Numbers
Cubes and Cube Roots
Playing with Numbers
- Arranging the Objects in Rows and Columns
- Generalized Form of Numbers
- Some Interesting Properties
- Letters for Digits (Cryptarithms)
- Divisibility by 10
- Divisibility by 2
- Divisibility by 5
- Divisibility by 3
- Divisibility by 6
- Divisibility by 11
- Divisibility by 4
Sets
- Concept of Sets
- Representation of a Set
- Cardinal Number of a Set
- Types of Sets
- Subset
- Proper Subset
- Number of Subsets and Proper Subsets of a Given Set
- Super Set
- Universal Set
- Complement of a Set
- Set Operations
- Difference of Two Sets
- Distributive Laws
- Venn Diagrams
Ratio and Proportion
Percent and Percentage
Profit, Loss and Discount
- Concept of Discount
- Overhead Expenses
- To Find S.P., When C.P. and Gain (Or Loss) Percent Are Given
- To Find C.P., When S.P. and Gain (Or Loss) Percent Are Given
- Concept of Discount
- Computation of Tax
- Goods and Service Tax (Gst)
- Gst Comprises of
Interest
- Calculation of Interest
- Concept of Compound Interest
- To Find the Principle (P); the Rate Percent (R) and the Time
- Interest Compounded Half Yearly
- Applications of Compound Interest Formula
Direct and Inverse Variations
- Variations
- Types of Variation
- Direct Variation
- Inverse Variation
- Concept for Unitary Method (With Only Direct Variation Implied)
- Concept of Arrow Method
- Time and Work
Algebra
Algebraic Expressions
- Algebraic Expressions
- Degree of Polynomial
- Product , Factor and Coefficient
- Like and Unlike Terms
- Combining like Terms
- Multiplying Monomial by Monomials
- Multiplying a Monomial by a Polynomial
- Multiplying a Polynomial by a Polynomial
- Dividing a Monomial by a Monomial
- Dividing a Polynomial by a Monomial
- Dividing a Polynomial by a Polynomial
- Simplification of Expressions
Identities
- Algebraic Identities
- Product of Sum and Difference of Two Terms
- Expansion Form of Numbers
- Important Formula of Expansion
- Cubes of Binomials
- Application of Formulae
Factorisation
- Factorisation by Taking Out Common Factors
- Factorisation by Taking Out Common Factors
- Factorisation by Grouping
- Factorisation by Difference of Two Squares
- Factorisation of Trinomials
- Factorising a Perfect Square Trinomial
- Factorising Completely
Linear Equations in One Variable
- Simple Linear Equations in One Variable
- Solving Linear Inequations
- Linear Equation in One Variable
- Equations Reducible to the Linear Form
Linear Inequations
- Introduction to linear equations in two variables
- Replacement Set and Solution Set
- Operation of Whole Numbers on Number Line
- Concept of Properties
Geometry
Understanding Shapes
- Different Types of Curves - Closed Curve, Open Curve, Simple Curve.
- Concept of Polygons
- Sum of Angles of a Polynomial
- Sum of Exterior Angles of a Polynomial
- Regular Polynomial
- Concept of Quadrilaterals
Special Types of Quadrilaterals
Constructions
- Introduction of Constructions
- Construction of an Angle
- To Construct an Angle Equal to Given Angle
- To Draw the Bisector of a Given Angle
- Construction of an angle bisector of an Angles of 60°,30°,90° and 45°
- Construction of Bisector of a Line
- The Perpendicular Bisector
- Construction of Parallel Lines
- Constructing a Quadrilateral
- Construction of Parallelograms
- Construction of a Rectangle When Its Length and Breadth Are Given.
- Construction of Rhombus
- Construction of Square
- Concept of Reflection Symmetry
Representing 3-D in 2-D
- 2dimensional Perspective of 3dimensional Objects
- Concept of Polyhedron
- Faces, Edges and Vertices
- Euler's Formula
- Concept of Polyhedron
- Nets for Building 3-d Shapes
Mensuration
Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon
Surface Area, Volume and Capacity
Data Handling (Statistics)
Data Handling
- Concept of Data Handling
- Collecting Data
- Frequency
- Raw Data, Arrayed Data and Frequency Distribution
- Constructing a Frequency Table
- Frequency Distribution Table
- Class Intervals and Class Limits
- Graphical Representation of Data
Probability
- Introduction
- The Perpendicular Bisector of a Line Segment
Notes
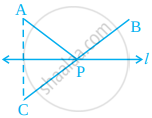
The perpendicular bisector of a line segment:
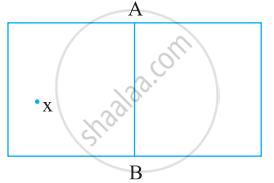
Fold a sheet of paper. Let `bar"AB"` be the fold. Place an ink-dot X, as shown, anywhere.
Find the image X' of X, with AB as the mirror line.
Let `bar"AB"` and `bar"XX’"` intersect at O.
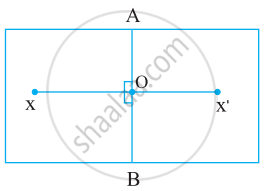
This means that `bar"AB" "divides" bar"XX’"` into two parts of equal length.
`bar"AB" "bisects" bar"XX’" or bar"AB" "is a bisector of" bar"XX’"`.
Hence, `bar"AB" "is the perpendicular bisector of" bar"XX’"`.
Construction using ruler and compasses:
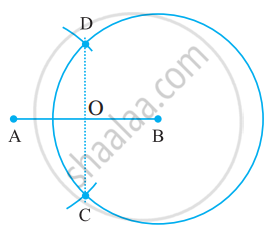
Step 1: Draw a line segment `bar"AB"` of any length.

Step 2: With A as the centre, using compasses, draw a circle. The radius of your circle should be more than half the length of `bar"AB"`.
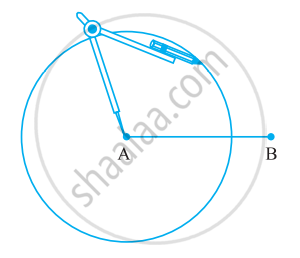
Step 3: With the same radius and with B as centre, draw another circle using compasses. Let it cut the previous circle at C and D.
Step 4: Join `bar"CD". "It cuts" bar"AB"` at O.
Use your divider to verify that O is the midpoint of `bar"AB"`.
Therefore, `bar"CD" "is the perpendicular bisector of" bar"AB".`