Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle executing simple harmonic motion comes to rest at the extreme positions. Is the resultant force on the particle zero at these positions according to Newton's first law?
उत्तर
No. The resultant force on the particle is maximum at the extreme positions.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A particle executes S.H.M. with a period of 10 seconds. Find the time in which its potential energy will be half of its total energy.
A small creature moves with constant speed in a vertical circle on a bright day. Does its shadow formed by the sun on a horizontal plane move in a sample harmonic motion?
Can the potential energy in a simple harmonic motion be negative? Will it be so if we choose zero potential energy at some point other than the mean position?
A pendulum clock that keeps correct time on the earth is taken to the moon. It will run
A pendulum clock keeping correct time is taken to high altitudes,
Which of the following quantities are always positive in a simple harmonic motion?
Suppose a tunnel is dug along a diameter of the earth. A particle is dropped from a point, a distance h directly above the tunnel. The motion of the particle as seen from the earth is
(a) simple harmonic
(b) parabolic
(c) on a straight line
(d) periodic
A simple pendulum of length 1 feet suspended from the ceiling of an elevator takes π/3 seconds to complete one oscillation. Find the acceleration of the elevator.
A closed circular wire hung on a nail in a wall undergoes small oscillations of amplitude 20 and time period 2 s. Find (a) the radius of the circular wire, (b) the speed of the particle farthest away from the point of suspension as it goes through its mean position, (c) the acceleration of this particle as it goes through its mean position and (d) the acceleration of this particle when it is at an extreme position. Take g = π2 m/s2.
A uniform disc of mass m and radius r is suspended through a wire attached to its centre. If the time period of the torsional oscillations be T, what is the torsional constant of the wire?
A simple pendulum is suspended from the roof of a school bus which moves in a horizontal direction with an acceleration a, then the time period is
A simple pendulum has a time period T1. When its point of suspension is moved vertically upwards according to as y = kt2, where y is the vertical distance covered and k = 1 ms−2, its time period becomes T2. Then, T `"T"_1^2/"T"_2^2` is (g = 10 ms−2)
Define the frequency of simple harmonic motion.
A spring is stretched by 5 cm by a force of 10 N. The time period of the oscillations when a mass of 2 kg is suspended by it is ______
Motion of a ball bearing inside a smooth curved bowl, when released from a point slightly above the lower point is ______.
- simple harmonic motion.
- non-periodic motion.
- periodic motion.
- periodic but not S.H.M.
What is the ratio of maxmimum acceleration to the maximum velocity of a simple harmonic oscillator?
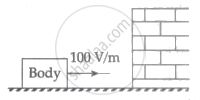
A body having specific charge 8 µC/g is resting on a frictionless plane at a distance 10 cm from the wall (as shown in the figure). It starts moving towards the wall when a uniform electric field of 100 V/m is applied horizontally toward the wall. If the collision of the body with the wall is perfectly elastic, then the time period of the motion will be ______ s.
Assume there are two identical simple pendulum clocks. Clock - 1 is placed on the earth and Clock - 2 is placed on a space station located at a height h above the earth's surface. Clock - 1 and Clock - 2 operate at time periods 4 s and 6 s respectively. Then the value of h is ______.
(consider the radius of earth RE = 6400 km and g on earth 10 m/s2)
