Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
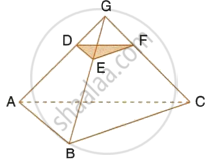
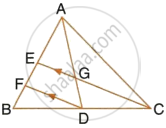
Given : AB || DE and BC || EF. Prove that :
- `(AD)/(DG) = (CF)/(FG)`
- ∆DFG ∼ ∆ACG
उत्तर
i. In ΔAGB, DE || AB, by Basic proportionality theorem
`(GD)/(DA) = (GE)/(EB)` ...(1)
In ΔGBC, EF || BC, by Basic proportionality theorem,
`(GE)/(EB) = (GF)/(FC)` ...(2)
From (1) and (2), we get
`(GD)/(DA) = (GF)/(FC)`
`(AD)/(DG) = (CF)/(FG)`
ii.
From (i), we have:
`(AD)/(DG) = (CF)/(FG)`
∠DGF = ∠AGC ...(Common)
∴ ΔDFG ∼ ΔACG ...(SAS similarity)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given: RS and PT are altitudes of ΔPQR. Prove that:
- ΔPQT ~ ΔQRS,
- PQ × QS = RQ × QT.
In the given figure, AX : XB = 3 : 5
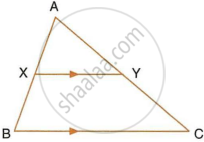
Find:
- the length of BC, if the length of XY is 18 cm.
- the ratio between the areas of trapezium XBCY and triangle ABC.
In the given triangle PQR, LM is parallel to QR and PM : MR = 3 : 4.
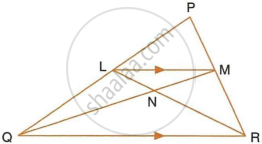
Calculate the value of ratio:
- `(PL)/(PQ)` and then `(LM)/(QR)`
- `"Area of ΔLMN"/"Area of ΔMNR"`
- `"Area of ΔLQM"/"Area of ΔLQN"`
In the following diagram, lines l, m and n are parallel to each other. Two transversals p and q intersect the parallel lines at points A, B, C and P, Q, R as shown.
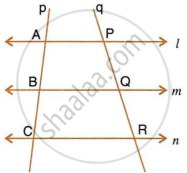
Prove that : `(AB)/(BC) = (PQ)/(QR)`
In the following figure, AD and CE are medians of ΔABC. DF is drawn parallel to CE. Prove that :
- EF = FB,
- AG : GD = 2 : 1
In the given figure, triangle ABC is similar to triangle PQR. AM and PN are altitudes whereas AX and PY are medians.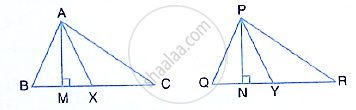 Prove that : `(AM)/(PN)=(AX)/(PY)`
Prove that : `(AM)/(PN)=(AX)/(PY)`
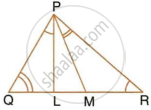
In a triangle PQR, L and M are two points on the base QR, such that ∠LPQ = ∠QRP and ∠RPM = ∠RQP. Prove that:
- ΔPQL ∼ ΔRPM
- QL × RM = PL × PM
- PQ2 = QR × QL
Two isosceles triangles have equal vertical angles. Show that the triangles are similar. If the ratio between the areas of these two triangles is 16 : 25, find the ratio between their corresponding altitudes.
The following figure shows a triangle ABC in which AD and BE are perpendiculars to BC and AC respectively.
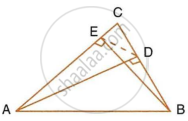
Show that:
- ΔADC ∼ ΔBEC
- CA × CE = CB × CD
- ΔABC ~ ΔDEC
- CD × AB = CA × DE
In the given figure, ABC is a right angled triangle with ∠BAC = 90°.
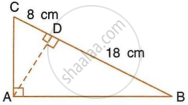
- Prove that : ΔADB ∼ ΔCDA.
- If BD = 18 cm and CD = 8 cm, find AD.
- Find the ratio of the area of ΔADB is to area of ΔCDA.
