Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Identify, with reason, if the following is a Pythagorean triplet.
(5, 12, 13)
उत्तर
In the triplet (5, 12, 13),
52 = 25,
122 = 144,
132 = 169
52 + 122 = 25 + 144 = 169
The square of the largest number is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two numbers.
∴ (5, 12, 13) is a pythagorean triplet.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the sides of a triangle are 6 cm, 8 cm and 10 cm, respectively, then determine whether the triangle is a right angle triangle or not.
In a right triangle ABC right-angled at C, P and Q are the points on the sides CA and CB respectively, which divide these sides in the ratio 2 : 1. Prove that
`(i) 9 AQ^2 = 9 AC^2 + 4 BC^2`
`(ii) 9 BP^2 = 9 BC^2 + 4 AC^2`
`(iii) 9 (AQ^2 + BP^2 ) = 13 AB^2`
In a ∆ABC, AD ⊥ BC and AD2 = BC × CD. Prove ∆ABC is a right triangle
Two poles of heights 6 m and 11 m stand on a plane ground. If the distance between the feet of the poles is 12 m, find the distance between their tops.
D and E are points on the sides CA and CB respectively of a triangle ABC right angled at C. Prove that AE2 + BD2 = AB2 + DE2
In an equilateral triangle ABC, D is a point on side BC such that BD = `1/3BC` . Prove that 9 AD2 = 7 AB2
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle in which ∠ABC> 90° and AD ⊥ CB produced. Prove that AC2 = AB2 + BC2 + 2BC.BD.
Which of the following can be the sides of a right triangle?
1.5 cm, 2 cm, 2.5 cm
In the case of right-angled triangles, identify the right angles.
Find the perimeter of the rectangle whose length is 40 cm and a diagonal is 41 cm.
Find the length of the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle if remaining sides are 9 cm and 12 cm.
In triangle ABC, AB = AC and BD is perpendicular to AC.
Prove that: BD2 - CD2 = 2CD × AD
Find the length of diagonal of the square whose side is 8 cm.
If P and Q are the points on side CA and CB respectively of ΔABC, right angled at C, prove that (AQ2 + BP2 ) = (AB2 + PQ2)
The sides of a certain triangle is given below. Find, which of them is right-triangle
6 m, 9 m, and 13 m
In a triangle ABC, AC > AB, D is the midpoint BC, and AE ⊥ BC. Prove that: AC2 = AD2 + BC x DE + `(1)/(4)"BC"^2`
In a triangle ABC, AC > AB, D is the midpoint BC, and AE ⊥ BC. Prove that: AC2 - AB2 = 2BC x ED
In a triangle ABC right angled at C, P and Q are points of sides CA and CB respectively, which divide these sides the ratio 2 : 1.
Prove that : 9(AQ2 + BP2) = 13AB2
In the figure, find AR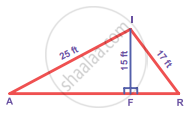
If the areas of two circles are the same, they are congruent.
The hypotenuse (in cm) of a right angled triangle is 6 cm more than twice the length of the shortest side. If the length of third side is 6 cm less than thrice the length of shortest side, then find the dimensions of the triangle.
