Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If A, B and C are interior angles of ΔABC, prove that sin`(("A" + "B")/2) = cos "C"/(2)`
उत्तर
Since A, B and C are interior angles of ΔABC,
A + B + C = 180°
⇒ A + B = 180° - C
Now,
L.H.S. = `sin (("A" + "B")/2)`
= `sin ((180° - "C")/2)`
= `sin(90° - "C"/2)`
= `cos "C"/(2)`
= R.H.S.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Solve the following equation for A, if 2cos2A = 1
Calculate the value of A, if (sec 2A - 1) (cosec 3A - 1) = 0
If sin 3A = 1 and 0 < A < 90°, find cos 2A
If θ = 30°, verify that: sin 3θ = 4sinθ . sin(60° - θ) sin(60° + θ)
If θ = 15°, find the value of: cos3θ - sin6θ + 3sin(5θ + 15°) - 2 tan23θ
If tan x° = `(5)/(12) . tan y° = (3)/(4)` and AB = 48m; find the length CD.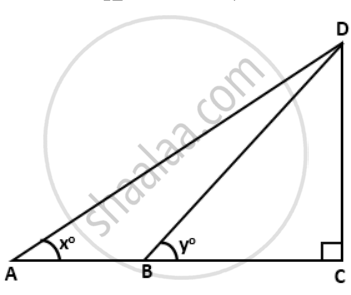
Evaluate the following: `(sec32° cot26°)/(tan64° "cosec"58°)`
Express each of the following in terms of trigonometric ratios of angles between 0° and 45°: cos84° + cosec69° - cot68°
Evaluate the following: `(3sin37°)/(cos53°) - (5"cosec"39°)/(sec51°) + (4tan23° tan37° tan67° tan53°)/(cos17° cos67° "cosec"73° "cosec"23°)`
Prove the following: sin58° sec32° + cos58° cosec32° = 2
