Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Prove the following: sin58° sec32° + cos58° cosec32° = 2
उत्तर
L.H.S.
= sin58° sec32° + cos58° cosec32°
= `sin(90° - 32°) xx (1)/(cos32°) + cos(90° - 32°) xx (1)/(sin32°)`
= `cos32° xx (1)/(cos32°) + sin32° xx (1)/(sin32°)`
= 1 + 1
= 2
= R.H.S.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If 2 sin x° - 1 = 0 and x° is an acute angle; find:
- sin x°
- x°
- cos x° and tan x°.
If sin 3A = 1 and 0 < A < 90°, find sin A
If 2 cos 2A = `sqrt3` and A is acute,
find:
(i) A
(ii) sin 3A
(iii) sin2 (75° - A) + cos2 (45° +A)
In ΔABC, ∠B = 90° , AB = y units, BC = `(sqrt3)` units, AC = 2 units and angle A = x°, find:
- sin x°
- x°
- tan x°
- use cos x° to find the value of y.
Calculate the value of A, if (sec 2A - 1) (cosec 3A - 1) = 0
If ΔABC is a right triangle such that ∠C = 90°, ∠A = 45° and BC =7units, find ∠B, AB and AC.
Find the length of AD. Given: ∠ABC = 60°, ∠DBC = 45° and BC = 24 cm.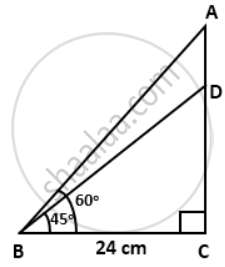
Find the value 'x', if: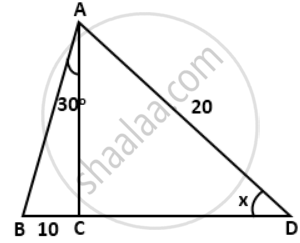
In the given figure; ∠B = 90°, ∠ADB = 30°, ∠ACB = 45° and AB = 24 m. Find the length of CD.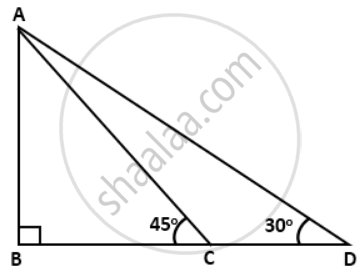
If secθ= cosec30° and θ is an acute angle, find the value of 4 sin2θ - 2 cos2θ.
