Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
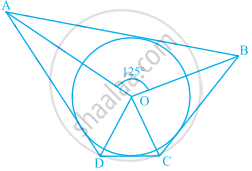
In figure, if ∠AOB = 125°, then ∠COD is equal to ______.
विकल्प
62.5°
45°
35°
55°
उत्तर
In figure, if ∠AOB = 125°, then ∠COD is equal to 55°.
Explanation:

ABCD is a quadrilateral circumscribing the circle
We know that, the opposite sides of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle subtend supplementary angles at the center of the circle.
So, we have
∠AOB + ∠COD = 180°
125° + ∠COD = 180°
∠COD = 55°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
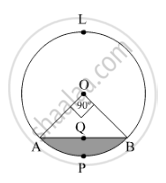
In fig. 5 is a chord AB of a circle, with centre O and radius 10 cm, that subtends a right angle at the centre of the circle. Find the area of the minor segment AQBP. Hence find the area of major segment ALBQA. (use π = 3.14)
In Figure 2, XP and XQ are two tangents to the circle with centre O, drawn from an external point X. ARB is another tangent, touching the circle at R. Prove that XA + AR = XB + BR ?

From a point Q, 13 cm away from the centre of a circle, the length of tangent PQ to the circle is 12 cm. The radius of the circle (in cm) is
Calculate the length of direct common tangent to two circles of radii 3cm and Bern with their centres 13cm apart.
Two equal chords AB and CD of a circle with center O, when produced meet at a point E, as shown in Fig. Prove that BE = DE and AE = CE.
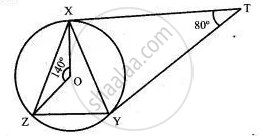
In the alongside, figure, O is the centre of the circumcircle of triangle XYZ. Tangents at X and Y intersect at T. Given ∠XTY = 80° and ∠XOZ = 140°. Calculate the value of ∠ZXY.
The distance between the centres of equal circles each of radius 3 cm is 10 cm. The length of a transverse tangent AB is ______
In the given figure, PT is a tangent at T to the circle with centre O. If ∠TPO = 25°, then x is equal to ______.

In the given figure O, is the centre of the circle. CE is a tangent to the circle at A. If ∠ABD = 26° find:
- ∠BDA
- ∠BAD
- ∠CAD
- ∠ODB

In the given diagram, PS and PT are the tangents to the circle. SQ || PT and ∠SPT = 80°. The value of ∠QST is ______.