Advertisements
Chapters
![NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 9 - Circles NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 9 - Circles - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-9_6:e75a1668572245b2974a4e6dc62140a3.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 9: Circles
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 9 of CBSE NCERT for Mathematics [English] Class 9.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 9 Circles EXERCISE 9.1 [Page 118]
Recall that two circles are congruent if they have the same radii. Prove that equal chords of congruent circles subtend equal angles at their centres.
Prove that if chords of congruent circles subtend equal angles at their centres, then the chords are equal.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 9 Circles EXERCISE 9.2 [Page 122]
Two circles of radii 5 cm and 3 cm intersect at two points and the distance between their centres is 4 cm. Find the length of the common chord.
If two equal chords of a circle intersect within the circle, prove that the segments of one chord are equal to corresponding segments of the other chord.
If two equal chords of a circle intersect within the circle, prove that the line joining the point of intersection to the centre makes equal angles with the chords.
If a line intersects two concentric circles (circles with the same centre) with centre O at A, B, C, and D, prove that AB = CD (see given figure).

Three girls Reshma, Salma and Mandip are playing a game by standing on a circle of radius 5m drawn in a park. Reshma throws a ball to Salma, Salma to Mandip, Mandip to Reshma. If the distance between Reshma and Salma and between Salma and Mandip is 6m each, what is the distance between Reshma and Mandip?
A circular park of radius 20m is situated in a colony. Three boys Ankur, Syed and David are sitting at equal distance on its boundary each having a toy telephone in his hands to talk each other. Find the length of the string of each phone.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 9 Circles EXERCISE 9.3 [Pages 127 - 129]
In the given figure, A, B and C are three points on a circle with centre O such that ∠BOC = 30° and ∠AOB = 60°. If D is a point on the circle other than the arc ABC, find ∠ADC.

A chord of a circle is equal to the radius of the circle. Find the angle subtended by the chord at a point on the minor arc and also at a point on the major arc.
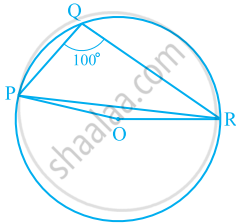
In the given figure, ∠PQR = 100°, where P, Q and R are points on a circle with centre O. Find ∠OPR.
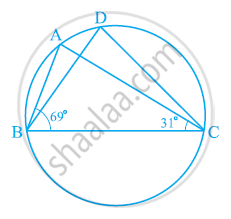
In the given figure, ∠ABC = 69°, ∠ACB = 31°, find ∠BDC.
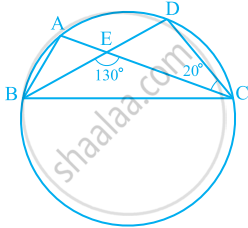
In the given figure, A, B, C and D are four points on a circle. AC and BD intersect at a point E such that ∠BEC = 130° and ∠ECD = 20°. Find ∠BAC.
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral whose diagonals intersect at a point E. If ∠DBC = 70°, ∠BAC is 30°, find ∠BCD. Further, if AB = BC, find ∠ECD.
If diagonals of a cyclic quadrilateral are diameters of the circle through the vertices of the quadrilateral, prove that it is a rectangle.
If non-parallel sides of a trapezium are equal, prove that it is cyclic.
Two circles intersect at two points B and C. Through B, two line segments ABD and PBQ are drawn to intersect the circles at A, D and P, Q respectively (see the given figure). Prove that ∠ACP = ∠QCD.

If circles are drawn taking two sides of a triangle as diameters, prove that the point of intersection of these circles lie on the third side.
ABC and ADC are two right triangles with common hypotenuse AC. Prove that ∠CAD = ∠CBD.
Prove that a cyclic parallelogram is a rectangle.
Solutions for 9: Circles
![NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 9 - Circles NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 9 - Circles - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-9_6:e75a1668572245b2974a4e6dc62140a3.jpg)
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 9 - Circles
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE 9 (Circles) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 9 Circles are Angle Subtended by a Chord at a Point, Perpendicular from the Centre to a Chord, Equal Chords and Their Distances from the Centre, Angle Subtended by an Arc of a Circle, Concept of Circle, Cyclic Quadrilateral, Circles Passing Through One, Two, Three Points, Angle Subtended by a Chord at a Point, Perpendicular from the Centre to a Chord, Equal Chords and Their Distances from the Centre, Angle Subtended by an Arc of a Circle, Concept of Circle, Cyclic Quadrilateral, Circles Passing Through One, Two, Three Points.
Using NCERT Mathematics [English] Class 9 solutions Circles exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Mathematics [English] Class 9 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 9, Circles Mathematics [English] Class 9 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
