Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the inverse relation R−1 in each of the cases:
(ii) R = {(x, y), : x, y ∈ N, x + 2y = 8}
उत्तर
(ii) R = {(x, y) : x, y ∈ N, x + 2y = 8}
On solving x + 2y = 8, we get:
x = 8 - 2y
On putting y = 1, we get x = 6.
On putting y = 2, we get x = 4.
On putting y = 3, we get x = 2.
∴ R = {(6, 1), (4, 2), (2, 3)}
Or,
R−1 = {(1, 6), (2, 4), (3, 2)}
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A = {1, 2, 3, 5} and B = {4, 6, 9}. Define a relation R from A to B by R = {(x, y): the difference between x and y is odd; x ∈ A, y ∈ B}. Write R in roster form.
The given figure shows a relationship between the sets P and Q. Write this relation
- in set-builder form.
- in roster form.
What is its domain and range?
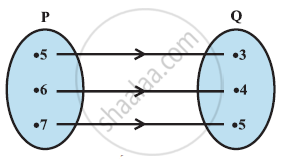
Determine the domain and range of the relations:
(i) R = {(a, b) : a ∈ N, a < 5, b = 4}
Let R be a relation from N to N defined by R = {(a, b) : a, b ∈ N and a = b2}. Is the statement true?
(a, b) ∈ R implies (b, a) ∈ R
Justify your answer in case.
For the relation R1 defined on R by the rule (a, b) ∈ R1 ⇔ 1 + ab > 0. Prove that: (a, b) ∈ R1 and (b , c) ∈ R1 ⇒ (a, c) ∈ R1 is not true for all a, b, c ∈ R.
Let R be a relation on N × N defined by
(a, b) R (c, d) ⇔ a + d = b + c for all (a, b), (c, d) ∈ N × N
Show that:
(ii) (a, b) R (c, d) ⇒ (c, d) R (a, b) for all (a, b), (c, d) ∈ N × N
If R is a relation defined on the set Z of integers by the rule (x, y) ∈ R ⇔ x2 + y2 = 9, then write domain of R.
If R is a relation from set A = (11, 12, 13) to set B = (8, 10, 12) defined by y = x − 3, then write R−1.
If A = {1, 2, 4}, B = {2, 4, 5}, C = {2, 5}, then (A − B) × (B − C) is
If A = [1, 2, 3], B = [1, 4, 6, 9] and R is a relation from A to B defined by 'x' is greater than y. The range of R is
A relation ϕ from C to R is defined by x ϕ y ⇔ |x| = y. Which one is correct?
If the set A has p elements, B has q elements, then the number of elements in A × B is
Write the relation in the Roster Form. State its domain and range
R1 = {(a, a2)/a is prime number less than 15}
Write the relation in the Roster Form. State its domain and range
R2 = `{("a", 1/"a") // 0 < "a" ≤ 5, "a" ∈ "N"}`
Answer the following:
If A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6} check if the following are relations from A to B. Also write its domain and range
R1 = {(1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6)}
Answer the following:
If A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6} check if the following are relations from A to B. Also write its domain and range
R2 = {(1, 5), (2, 4), (3, 6)}
Answer the following:
Find R : A → A when A = {1, 2, 3, 4} such that R = (a, b)/a − b = 10}
Let A = {1, 2, 3, 7} and B = {3, 0, –1, 7}, the following is relation from A to B?
R3 = {(2, –1), (7, 7), (1, 3)}
Let A = {1, 2, 3, 7} and B = {3, 0, –1, 7}, the following is relation from A to B?
R4 = {(7, –1), (0, 3), (3, 3), (0, 7)}
Represent the given relation by
(a) an arrow diagram
(b) a graph and
(c) a set in roster form, wherever possible
{(x, y) | x = 2y, x ∈ {2, 3, 4, 5}, y ∈ {1, 2, 3, 4}
Multiple Choice Question :
If there are 1024 relation from a set A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} to a set B, then the number of elements in B is
Find the domain of the function f(x) = `sqrt(1 + sqrt(1 - sqrt(1 - x^2)`
Discuss the following relation for reflexivity, symmetricity and transitivity:
Let A be the set consisting of all the members of a family. The relation R defined by “aRb if a is not a sister of b”
Let A = {a, b, c} and R = {(a, a), (b, b), (a, c)}. Write down the minimum number of ordered pairs to be included to R to make it equivalence
On the set of natural numbers let R be the relation defined by aRb if 2a + 3b = 30. Write down the relation by listing all the pairs. Check whether it is reflexive
On the set of natural numbers let R be the relation defined by aRb if 2a + 3b = 30. Write down the relation by listing all the pairs. Check whether it is transitive
Let A = {a, b, c}. What is the equivalence relation of smallest cardinality on A? What is the equivalence relation of largest cardinality on A?
In the set Z of integers, define mRn if m − n is divisible by 7. Prove that R is an equivalence relation
Choose the correct alternative:
Let R be the set of all real numbers. Consider the following subsets of the plane R × R: S = {(x, y) : y = x + 1 and 0 < x < 2} and T = {(x, y) : x − y is an integer} Then which of the following is true?
Choose the correct alternative:
Let f : R → R be defined by f(x) = 1 − |x|. Then the range of f is
Find the domain and range of the relation R given by R = {(x, y) : y = `x + 6/x`; where x, y ∈ N and x < 6}.
Is the following relation a function? Justify your answer
R1 = `{(2, 3), (1/2, 0), (2, 7), (-4, 6)}`
A relation on the set A = {x : |x| < 3, x ∈ Z}, where Z is the set of integers is defined by R = {(x, y) : y = |x| ≠ –1}. Then the number of elements in the power set of R is ______.
Let N denote the set of all natural numbers. Define two binary relations on N as R1 = {(x, y) ∈ N × N : 2x + y = 10} and R2 = {(x, y) ∈ N × N : x + 2y = 10}. Then ______.
