Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If cot α = `1/2`, sec β = `(-5)/3`, where π < α < `(3pi)/2 and pi/2` < β < π, find the value of tan(α + β). State the quadrant in which α + β terminates.
उत्तर
Given that cot α = `1/2` where π < α < `(3pi)/2` (i.e,. α lies in third quadrant)
tan α = `1/(1/2)` = 2 [∵ In 3rd quadrant tan α is positive]
Also given that sec β = `(-5)/3` where `pi/2` < β < π (i.e., β lies in second quadrant cos β and tan β are negative)
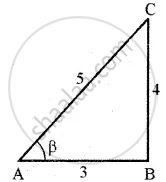
BC = `sqrt(5^2 - 3^2)` = 4
Now cos β = `1/(sec beta) = (-3)/5`
∴ tan β = `(- "Opposite side")/("Hypotenuse") = - 4/3`
Consider tan(α + β) = `(tan alpha + tan beta)/(1 - tan alpha tan beta)`
`= (2 + ((-4)/3))/(1 - 2((-4)/3))`
`= ((2xx 3 - 4)/3)/(1 + 8/3)`
`= (2/3)/(11/3)`
`= 2/11`
tan (α + β) = `2/11` which is positive.
α + β terminates in first quandrant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the value of the following:
cosec 15º
Find the value of the following:
`sin pi/4 cos pi/12 + cos pi/4 sin pi/12`
Find the value of the following:
cos2 15° – sin2 15°
If sin A = `3/5`, 0 < A < `pi/2` and cos B = `(-12)/13`, π < B < `(3pi)/2`, find the values of the following:
- cos(A + B)
- sin(A – B)
- tan(A – B)
If cos A = `13/14` and cos B = `1/7` where A, B are acute angles prove that A – B = `pi/3`
If tan θ = 3 find tan 3θ
Prove that `(sin ("B - C"))/(cos "B" cos "C") + (sin ("C - A"))/(cos "C" cos "A") + (sin ("A - B"))/(cos "A" cos "B")` = 0
If tan A – tan B = x and cot B – cot A = y prove that cot(A – B) = `1/x + 1/y`.
The value of `(2 tan 30^circ)/(1 + tan^2 30^circ)` is:
If p sec 50° = tan 50° then p is:
