Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the below figure, If AB || CD, find the value of x.
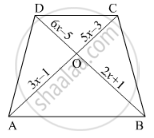
उत्तर
`rArr(3x-1)/(5x-3)=(2x+1)/(6x-5)`
⇒ (3x – 1) (6x – 5) = (2x + 1) (5x – 3)
⇒ 3x (6x – 5) – 1(6x – 5) = 2x (5x – 3) + 1 (5x – 3)
⇒ 18𝑥2 − 15𝑥 − 6𝑥 + 5 = 10𝑥2 − 6𝑥 + 5𝑥 − 3
⇒ 8𝑥2 − 20𝑥 + 8 = 0
⇒ 4(2𝑥2 − 5𝑥 + 2) = 0
⇒ 2𝑥2 − 4𝑥 − 1𝑥 + 2 = 0
⇒ 2𝑥(𝑥 − 2) − 1(𝑥 − 2) = 0
⇒ (2𝑥 − 1)(𝑥 − 2) = 0
⇒ 2x – 1 = 0 or x – 2 = 0
⇒ 𝑥 = 1/2 or 𝑥 = 2
𝑥 = 1/2 is not possible, because, OC = 5x – 3
`= 5(1/2) - 3`
`=(5-6)/2=-1/2`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = BC. If P, Q, R, S be the mid-points of AB, AC, CD and BD respectively, show that PQRS is a rhombus.
In ∆ABC, P and Q are points on sides AB and AC respectively such that PQ || BC. If AP = 4 cm, PB = 6 cm and PQ = 3 cm, determine BC.
In ∆ABC, P and Q are points on sides AB and AC respectively such that PQ || BC. If AP = 3 cm, PB = 5 cm and AC = 8 cm, find AQ.
In ∆ABC, D and E are points on sides AB and AC respectively such that AD ✕ EC = AE ✕ DB. Prove that DE || BC.
Sides of two similar triangles are in the ratio 4 : 9. Areas of these triangles are in the ratio.
If ∆ABC and ∆DEF are two triangles such tha\[\frac{AB}{DE} = \frac{BC}{EF} = \frac{CA}{FD} = \frac{2}{5}\] , then Area (∆ABC) : Area (∆DEF) =
XY is drawn parallel to the base BC of a ∆ABC cutting AB at X and AC at Y. If AB = 4 BX and YC = 2 cm, then AY =
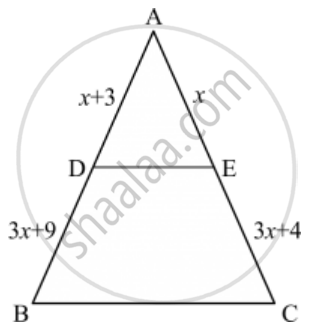
In the given figure, the value of x for which DE || AB is
Two isosceles triangles have equal angles and their areas are in the ratio 16 : 25. The ratio of their corresponding heights is
In a ∆ABC, ∠A = 90°, AB = 5 cm and AC = 12 cm. If AD ⊥ BC, then AD =
