Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show that the function f: R → R given by f(x) = x3 is injective.
उत्तर १
f: R → R is given as f(x) = x3.
Suppose f(x) = f(y), where x, y ∈ R.
⇒ x3 = y3 ... (1)
Now, we need to show that x = y.
Suppose x ≠ y, their cubes will also not be equal.
⇒ x3 ≠ y3
However, this will be a contradiction to (1).
∴ x = y
Hence, f is injective.
उत्तर २
Let x1, x2 ∈ R be such that
`f (x_1) = f(x_2) = x_1^3 = x_2^3`
= x1 = x2
∴ f is one-one.
Hence, f(x) = x3 is injective.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: R → R given by f(x) = x2
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: N → N given by f(x) = x3
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. Show that f is one-one.
Show that function f: R `rightarrow` {x ∈ R : −1 < x < 1} defined by f(x) = `x/(1 + |x|)`, x ∈ R is one-one and onto function.
Find the number of all onto functions from the set {1, 2, 3, …, n} to itself.
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto?
f2 = {(2, a), (3, b), (4, c)} ; A = {2, 3, 4}, B = {a, b, c}
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto ?
f3 = {(a, x), (b, x), (c, z), (d, z)} ; A = {a, b, c, d,}, B = {x, y, z}.
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Z → Z, defined by f(x) = x2 + x
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 1 + x2
Let A = [-1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following function from A to itself is one-one, onto or bijective : `f (x) = x/2`
Show that the logarithmic function f : R0+ → R given by f (x) loga x ,a> 0 is a bijection.
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = x and g(x) = |x| .
Find fog (2) and gof (1) when : f : R → R ; f(x) = x2 + 8 and g : R → R; g(x) = 3x3 + 1.
If f : A → B and g : B → C are one-one functions, show that gof is a one-one function.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = x2 g(x) = cos x .
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = |x|, g (x) = sin x .
If f(x) = 2x + 5 and g(x) = x2 + 1 be two real functions, then describe each of the following functions:
(1) fog
(2) gof
(3) fof
(4) f2
Also, show that fof ≠ f2
Find f −1 if it exists : f : A → B, where A = {0, −1, −3, 2}; B = {−9, −3, 0, 6} and f(x) = 3 x.
Consider f : R+ → [−5, ∞) given by f(x) = 9x2 + 6x − 5. Show that f is invertible with `f^-1 (x) = (sqrt (x +6)-1)/3 .`
If f : A → A, g : A → A are two bijections, then prove that fog is an injection ?
Which of the following graphs represents a one-one function?
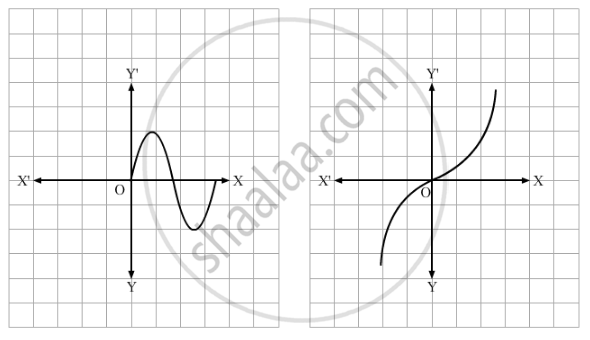
Which one the following relations on A = {1, 2, 3} is a function?
f = {(1, 3), (2, 3), (3, 2)}, g = {(1, 2), (1, 3), (3, 1)} [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let the function
\[f : R - \left\{ - b \right\} \to R - \left\{ 1 \right\}\]
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{x + a}{x + b}, a \neq b .\text{Then},\]
Let
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : - 1 \leq x \leq 1 \right\} = B\] Then, the mapping\[f : A \to \text{B given by} f\left( x \right) = x\left| x \right|\] is
If the function\[f : R \to \text{A given by} f\left( x \right) = \frac{x^2}{x^2 + 1}\] is a surjection, then A =
The function
Let \[f\left( x \right) = x^2 and g\left( x \right) = 2^x\] Then, the solution set of the equation
If \[g\left( x \right) = x^2 + x - 2\text{ and} \frac{1}{2} gof\left( x \right) = 2 x^2 - 5x + 2\] is equal to
Let f: R → R be defined by f(x) = 3x – 4. Then f–1(x) is given by ______.
Let f : R → R be a function defined by f(x) `= ("e"^abs"x" - "e"^-"x")/("e"^"x" + "e"^-"x")` then f(x) is
Let R be a relation on the set L of lines defined by l1 R l2 if l1 is perpendicular to l2, then relation R is ____________.
Given a function If as f(x) = 5x + 4, x ∈ R. If g : R → R is inverse of function ‘f then
A function f: x → y is said to be one – one (or injective) if:
The solution set of the inequation log1/3(x2 + x + 1) + 1 > 0 is ______.
Consider a set containing function A= {cos–1cosx, sin(sin–1x), sinx((sinx)2 – 1), etan{x}, `e^(|cosx| + |sinx|)`, sin(tan(cosx)), sin(tanx)}. B, C, D, are subsets of A, such that B contains periodic functions, C contains even functions, D contains odd functions then the value of n(B ∩ C) + n(B ∩ D) is ______ where {.} denotes the fractional part of functions)
Difference between the greatest and least value of f(x) = `(1 + (cos^-1x)/π)^2 - (1 + (sin^-1x)/π)^2` is ______.
Let a function `f: N rightarrow N` be defined by
f(n) = `{:[(2n",", n = 2"," 4"," 6"," 8","......),(n - 1",", n = 3"," 7"," 11"," 15","......),((n + 1)/2",", n = 1"," 5"," 9"," 13","......):}`
then f is ______.
The function f(x) = [x], where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x; is continuous at ______.
