Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If \[g\left( x \right) = x^2 + x - 2\text{ and} \frac{1}{2} gof\left( x \right) = 2 x^2 - 5x + 2\] is equal to
पर्याय
\[2 x - 3\]
\[2 x + 3\]
\[2 x^2 + 3x + 1\]
2 \[x^2 - 3x - 1\]
उत्तर
We will solve this problem by the trial-and-error method.
Let us check option (a) first. \[\text{If f}\left( x \right) = 2x - 3\]
\[\frac{1}{2}\left( gof \right)\left( x \right) = g\left( f\left( x \right) \right)\]
\[ = \frac{1}{2}g\left( 2x - 3 \right)\]
\[ = \frac{1}{2}\left[ \left( 2x - 3 \right)^2 + \left( 2x - 3 \right) - 2 \right]\]
\[ = \frac{1}{2}\left[ 4 x^2 + 9 - 12x + 2x - 3 - 2 \right]\]
\[ = \frac{1}{2}\left[ 4 x^2 - 10x + 4 \right]\]
\[ = 2 x^2 - 5x + 2\]
The given condition is satisfied by (a).
So, the answer is (a).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: N → N given by f(x) = x2
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: Z → Z given by f(x) = x2
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. Show that f is one-one.
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto ?
f3 = {(a, x), (b, x), (c, z), (d, z)} ; A = {a, b, c, d,}, B = {x, y, z}.
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = |x|
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Q → Q, defined by f(x) = x3 + 1
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = `x/(x^2 +1)`
If f : A → B is an injection, such that range of f = {a}, determine the number of elements in A.
Show that the function f : R − {3} → R − {2} given by f(x) = `(x-2)/(x-3)` is a bijection.
Given A = {2, 3, 4}, B = {2, 5, 6, 7}. Construct an example of each of the following:
(i) an injective map from A to B
(ii) a mapping from A to B which is not injective
(iii) a mapping from A to B.
Show that f : R→ R, given by f(x) = x — [x], is neither one-one nor onto.
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be defined by f(x) = x2 and g(x) = x + 1. Show that fog ≠ gof.
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be defined by f(x) = x + 1 and g (x) = x − 1. Show that fog = gof = IR.
Verify associativity for the following three mappings : f : N → Z0 (the set of non-zero integers), g : Z0 → Q and h : Q → R given by f(x) = 2x, g(x) = 1/x and h(x) = ex.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = ex g(x) = loge x .
Consider f : R+ → [−5, ∞) given by f(x) = 9x2 + 6x − 5. Show that f is invertible with `f^-1 (x) = (sqrt (x +6)-1)/3 .`
If f : Q → Q, g : Q → Q are two functions defined by f(x) = 2 x and g(x) = x + 2, show that f and g are bijective maps. Verify that (gof)−1 = f−1 og −1.
If f : R → (0, 2) defined by `f (x) =(e^x - e^(x))/(e^x +e^(-x))+1`is invertible , find f-1.
Let f be a function from R to R, such that f(x) = cos (x + 2). Is f invertible? Justify your answer.
If A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {a, b, c, d}, define any four bijections from A to B. Also give their inverse functions.
If f : A → A, g : A → A are two bijections, then prove that fog is an injection ?
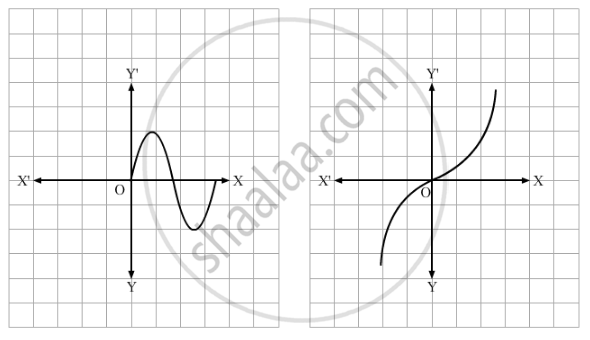
Which of the following graphs represents a one-one function?
If f : C → C is defined by f(x) = x2, write f−1 (−4). Here, C denotes the set of all complex numbers.
If f : C → C is defined by f(x) = (x − 2)3, write f−1 (−1).
Let \[f : \left[ - \frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2} \right] \to\] A be defined by f(x) = sin x. If f is a bijection, write set A.
Let
\[f : R - \left\{ n \right\} \to R\]
Let \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{1 - x} . \text{Then}, \left\{ f o \left( fof \right) \right\} \left( x \right)\]
Let \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{\alpha x}{x + 1}, x \neq - 1\] Then, for what value of α is \[f \left( f\left( x \right) \right) = x?\]
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
If the set A contains 5 elements and the set B contains 6 elements, then the number of one-one and onto mappings from A to B is
Which function is used to check whether a character is alphanumeric or not?
Write about strcmp() function.
Let A = {0, 1} and N be the set of natural numbers. Then the mapping f: N → A defined by f(2n – 1) = 0, f(2n) = 1, ∀ n ∈ N, is onto.
Let f : R → R be defind by f(x) = `1/"x" AA "x" in "R".` Then f is ____________.
Which of the following functions from Z into Z is bijective?
Let f : [0, ∞) → [0, 2] be defined by `"f" ("x") = (2"x")/(1 + "x"),` then f is ____________.
If N be the set of all-natural numbers, consider f: N → N such that f(x) = 2x, ∀ x ∈ N, then f is ____________.
Let f: R→R be defined as f(x) = 2x – 1 and g: R – {1}→R be defined as g(x) = `(x - 1/2)/(x - 1)`. Then the composition function f (g(x)) is ______.
Let x is a real number such that are functions involved are well defined then the value of `lim_(t→0)[max{(sin^-1 x/3 + cos^-1 x/3)^2, min(x^2 + 4x + 7)}]((sin^-1t)/t)` where [.] is greatest integer function and all other brackets are usual brackets.
Let f(n) = `[1/3 + (3n)/100]n`, where [n] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to n. Then `sum_(n = 1)^56f(n)` is equal to ______.
If f : R `rightarrow` R is defined by `f(x) = (2x - 7)/4`, show that f(x) is one-one and onto.
