Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The electric field in a region is given by `vec"E" = ("E"_0 "x")/"l" vec"i".`
Find the charge contained inside the cubical volume bound by the surfaces
x =0, x =a, y=0, y=a, z=0 and z=a. Take
`"E"_0 = 5 xx 10^3 "N""C"^-1 , "l" =2 "cm" " and" " a" = 1 "cm" `
उत्तर
Given:
Electric field strength, `vec"E" = ("E"_0"x")/"l" hat"i"`
Length, l = 2 cm
Edge of the cube, a = 1 cm
E0 =5.0 × 103 N/C

It is observed that the flux passes mainly through the surfaces ABCD and EFGH. The surfaces AEFB and CHGD are parallel to the electric field. So, electric flux for these surfaces is zero.
The electric field intensity at the surface EFGH will be zero.
If the charge is inside the cube, then equal flux will pass through the two parallel surfaces ABCD and EFGH. We can calculate flux passing only through one surface. Thus,
`vec"E" = ("E"_0"x")/"l" hat"i"`
At EFGH, x = 0; thus, the electric field at EFGH is zero.
At ABCD, x = a; thus, the electric field at ABCD is ` vec"E" = ("E"_0"a")/"l" hat "i"`
The net flux through the whole cube is only through the side ABCD and is given by
`phi = vec"E" . vec "A" = (("E"_0"a")/"l" hat"i") . ("a" hat"i") = ("E"_0"a"^2)/"l".`
Net flux = `phi =( 5 xx 10^3)/( 2 xx 10^-2) xx ( 1 xx 10 ^-2)^2 "N""m"^2 // "C" = 2.5 "Nm"^2 // "C"`
Thus the net charge,
q = ∈0 `phi`
q = 8.85 × 10 -12 × 2.5
q =22.125 ×10-13
q =2.2125 ×10 -12 C
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Plot a graph showing the variation of resistivity of a conductor with temperature.
Why is the potential inside a hollow spherical charged conductor constant and has the same value of as on its surface?
A charge Q is uniformly distributed over a large plastic plate. The electric field at a point P close to the centre of the plate is 10 V m−1. If the plastic plate is replaced by a copper plate of the same geometrical dimensions and carrying the same charge Q, the electric field at the point P will become
A metallic particle with no net charge is placed near a finite metal plate carrying a positive charge. The electric force on the particle will be
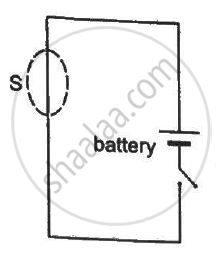
A closed surface S is constructed around a conducting wire connected to a battery and a switch in the following figure. As the switch is closed, the free electrons in the wire start moving along the wire. In any time interval, the number of electrons entering the closed surface S is equal to the number of electrons leaving it. On closing the switch, the flux of the electric field through the closed surface
(a) is increased
(b) is decreased
(c) remains unchanged
(d) remains zero
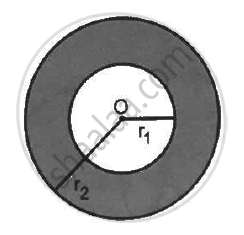
A charge Q is distributed uniformly within the material of a hollow sphere of inner and outer radii r1 and r2 (see the figure). Find the electric field at a point P at a distance x away from the centre for r1 < x < r. Draw a rough graph showing the electric field as a function of x for 0 < x < 2r2 (see the figure).
Consider the following very rough model of a beryllium atom. The nucleus has four protons and four neutrons confined to a small volume of radius 10−15 m. The two 1 selectrons make a spherical charge cloud at an average distance of 1⋅3 ×10−11 m from the nucleus, whereas the two 2 s electrons make another spherical cloud at an average distance of 5⋅2 × 10−11 m from the nucleus. Find three electric fields at (a) a point just inside the 1 s cloud and (b) a point just inside the 2 s cloud.
A long cylindrical wire carries a positive charge of linear density 2.0 × 10-8 C m -1 An electron revolves around it in a circular path under the influence of the attractive electrostatic force. Find the kinetic energy of the electron. Note that it is independent of the radius.
A non-conducting sheet of large surface area and thickness d contains a uniform charge distribution of density ρ. Find the electric field at a point P inside the plate, at a distance x from the central plane. Draw a qualitative graph of E against x for 0 < x < d.
One end of a 10 cm long silk thread is fixed to a large vertical surface of a charged non-conducting plate and the other end is fastened to a small ball of mass 10 g and a charge of 4.0× 10-6 C. In equilibrium, the thread makes an angle of 60° with the vertical (a) Find the tension in the string in equilibrium. (b) Suppose the ball is slightly pushed aside and released. Find the time period of the small oscillations.
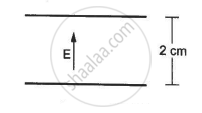
An electric field of magnitude 1000 NC−1 is produced between two parallel plates with a separation of 2.0 cm, as shown in the figure. (a) What is the potential difference between the plates? (b) With what minimum speed should an electron be projected from the lower place in the direction of the field, so that it may reach the upper plate? (c) Suppose the electron is projected from the lower place with the speed calculated in part (b). The direction of projection makes an angle of 60° with the field. Find the maximum height reached by the electron.
A uniform field of 2.0 NC−1 exists in space in the x-direction. (a) Taking the potential at the origin to be zero, write an expression for the potential at a general point (x, y, z). (b) At which point, the potential is 25 V? (c) If the potential at the origin is taken to be 100 V, what will be the expression for the potential at a general point? (d) What will be the potential at the origin if the potential at infinity is taken to be zero? Is it practical to choose the potential at infinity to be zero?
Draw equipotential surfaces corresponding to a uniform electric field in the z-directions.
When a comb rubbed with dry hair attracts pieces of paper. This is because the ______.
The force per unit charge is known as ______.
Pick out the statement which is incorrect
