Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following functions from
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : - 1 \leq x \leq 1 \right\}\]
पर्याय
\[f\left( x \right) = |x|\]
\[f\left( x \right) = \sin\frac{\pi x}{2}\]
\[f\left( x \right) = \sin\frac{\pi x}{4}\]
None of these
उत्तर
\[f\left( x \right) = \sin\frac{\pi x}{2}\]
It is clear that f(x) is one-one.
\[\text{Range of f} = \left[ \sin\frac{\pi\left( - 1 \right)}{2}, \sin\frac{\pi\left( 1 \right)}{2} \right] = \left[ \sin \frac{- \pi}{2}, \sin\frac{\pi}{2} \right] = \left[ - 1, 1 \right] = A = \text{Co domain of f}\]
⇒ f is onto.
So, f is a bijection.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: Z → Z given by f(x) = x2
Let f: R → R be defined as f(x) = x4. Choose the correct answer.
Find the number of all onto functions from the set {1, 2, 3, …, n} to itself.
Let f: R → R be the Signum Function defined as
f(x) = `{(1,x>0), (0, x =0),(-1, x< 0):}`
and g: R → R be the Greatest Integer Function given by g(x) = [x], where [x] is greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then does fog and gof coincide in (0, 1]?
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto ?
f3 = {(a, x), (b, x), (c, z), (d, z)} ; A = {a, b, c, d,}, B = {x, y, z}.
Set of ordered pair of a function? If so, examine whether the mapping is injective or surjective :{(x, y) : x is a person, y is the mother of x}
If A = {1, 2, 3}, show that a one-one function f : A → A must be onto.
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be defined by f(x) = x + 1 and g (x) = x − 1. Show that fog = gof = IR.
If f : A → B and g : B → C are onto functions, show that gof is a onto function.
If f(x) = 2x + 5 and g(x) = x2 + 1 be two real functions, then describe each of the following functions:
(1) fog
(2) gof
(3) fof
(4) f2
Also, show that fof ≠ f2
Let f : R `{- 4/3} `- 43 →">→ R be a function defined as f(x) = `(4x)/(3x +4)` . Show that f : R - `{-4/3}`→ Rang (f) is one-one and onto. Hence, find f -1.
Let f : [−1, ∞) → [−1, ∞) be given by f(x) = (x + 1)2 − 1, x ≥ −1. Show that f is invertible. Also, find the set S = {x : f(x) = f−1 (x)}.
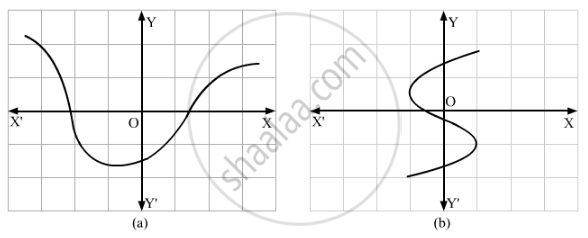
Which one of the following graphs represents a function?
Let f be a function from C (set of all complex numbers) to itself given by f(x) = x3. Write f−1 (−1).
If f : {5, 6} → {2, 3} and g : {2, 3} → {5, 6} are given by f = {(5, 2), (6, 3)} and g = {(2, 5), (3, 6)}, then find fog. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let f : R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 4x − 3 for all x ∈ R Then write f . [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
If the mapping f : {1, 3, 4} → {1, 2, 5} and g : {1, 2, 5} → {1, 3}, given by f = {(1, 2), (3, 5), (4, 1)} and g = {(2, 3), (5, 1), (1, 3)}, then write fog. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let
f : R → R be given by
\[f\left( x \right) = \left[ x^2 \right] + \left[ x + 1 \right] - 3\]
where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then, f(x) is
(d) one-one and onto
A function f from the set of natural numbers to integers defined by
`{([n-1]/2," when n is odd" is ),(-n/2,when n is even ) :}`
If the function\[f : R \to \text{A given by} f\left( x \right) = \frac{x^2}{x^2 + 1}\] is a surjection, then A =
Let
\[f : R \to R\] be given by \[f\left( x \right) = x^2 - 3\] Then, \[f^{- 1}\] is given by
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
If the set A contains 7 elements and the set B contains 10 elements, then the number one-one functions from A to B is
Let A = R − (2) and B = R − (1). If f: A ⟶ B is a function defined by`"f(x)"=("x"-1)/("x"-2),` how that f is one-one and onto. Hence, find f−1.
If f(x) = `(x+3)/(4x−5) , "g"(x) = (3+5x)/(4x−1)` then verify that `("fog") (x)` = x.
Show that the function f: R → R defined by f(x) = `x/(x^2 + 1)`, ∀ ∈ + R , is neither one-one nor onto
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
g = {(1, 4), (2, 4), (3, 4)}
Let f: R → R be defined by f(x) = `1/x` ∀ x ∈ R. Then f is ______.
Let f : R → R be a function defined by f(x) `= ("e"^abs"x" - "e"^-"x")/("e"^"x" + "e"^-"x")` then f(x) is
Students of Grade 9, planned to plant saplings along straight lines, parallel to each other to one side of the playground ensuring that they had enough play area. Let us assume that they planted one of the rows of the saplings along the line y = x − 4. Let L be the set of all lines which are parallel on the ground and R be a relation on L.
Answer the following using the above information.
- The function f: R → R defined by f(x) = x − 4 is ____________.
Raji visited the Exhibition along with her family. The Exhibition had a huge swing, which attracted many children. Raji found that the swing traced the path of a Parabola as given by y = x2.
Answer the following questions using the above information.
- Let : N → R be defined by f(x) = x2. Range of the function among the following is ____________.
Let f: R → R defined by f(x) = x4. Choose the correct answer
Function f: R → R, defined by f(x) = `x/(x^2 + 1)` ∀ x ∈ R is not
Consider a function f: `[0, pi/2] ->` R, given by f(x) = sinx and `g[0, pi/2] ->` R given by g(x) = cosx then f and g are
Prove that the function f is surjective, where f: N → N such that `f(n) = {{:((n + 1)/2",", if "n is odd"),(n/2",", if "n is even"):}` Is the function injective? Justify your answer.
Number of integral values of x satisfying the inequality `(3/4)^(6x + 10 - x^2) < 27/64` is ______.
Let f(x) = ax (a > 0) be written as f(x) = f1(x) + f2(x), where f1(x) is an even function and f2(x) is an odd function. Then f1(x + y) + f1(x – y) equals ______.
Let A = R – {2} and B = R – {1}. If f: A `→` B is a function defined by f(x) = `(x - 1)/(x - 2)` then show that f is a one-one and an onto function.
