Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A u-tube is made up of capillaries of bore 1 mm and 2 mm respectively. The tube is held vertically and partially filled with a liquid of surface tension 49 dyne/cm and zero angles of contact. Calculate the density of the liquid, if the difference in the levels of the meniscus is 1.25 cm. take g = 980 cm/s2
Solution
Let ‘r1’ be the radius of one bore and ‘r2’ be the radius of the second bore of the U-tube. Then, if ‘h1’ and ‘h2’ are the height of water on two sides, then
h1 = `(2T cosθ)/(r_1ρg)` ..........(i)
and h2 = `(2T cosθ)/(r_2ρg)` .................(ii)
Subtracting equation (ii) from equation (i),
h1 - h2 = `(2T cosθ)/(r_1ρg) - (2T cosθ)/(r_2ρg) = (2T cosθ)/(ρg)[1/r_1 - 1/r_2]`
∴ ρ = `(2Tcosθ)/((h_1 - h_2)g)[1/r_1 - 1/r_2]`
Given: T = 49 dyne/cm, θ = 0°,
h1 − h2 = 1.25 cm, g = 980 cm/s2
r1 = `1/2` mm = 0.5 mm = 5 × 10-2 cm
r2 = `2/2` mm = 1 mm = 10-1 cm
∴ ρ = `(2 xx 49 xx cos0^circ)/(1.25 xx 980) xx [1/(5 xx 10^-2) - 1/10^-1]`
= `1/12.5[20 - 10]`
= `10/12.5 = 1/1.25`
Using reciprocal table,
ρ = 0.8 g/cm3
The density of liquid is ρ = 0.8 g/cm3.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Derive an expression for excess pressure inside a drop of liquid.
A raindrop of diameter 4 mm is about to fall on the ground. Calculate the pressure inside the raindrop. [Surface tension of water T = 0.072 N/m, atmospheric pressure = 1.013 x 105 N/m2 ]
In which of the following substances, surface tension increases with increase in temperature ?
- Copper
- Molten copper
- Iron
- Molten iron
'n' droplets of equal size of radius r coalesce to form a bigger drop of radius R. The energy liberated is equal to...................
(T =Surface tension of water)
`(a) 4piR^2T[n^(1/3)-1]`
`(b) 4pir^2T[n^(1/3)-1]`
`(c) 4piR^2T[n^(2/3)-1]`
`(d)4 pir^2T[n^(2/3)-1]`
Mercury has an angle of contact equal to 140° with soda lime glass. A narrow tube of radius 1.00 mm made of this glass is dipped in a trough containing mercury. By what amount does the mercury dip down in the tube relative to the liquid surface outside? Surface tension of mercury at the temperature of the experiment is 0.465 N m–1. Density of mercury = 13.6 × 103 kg m–3
Mercury has an angle of contact equal to 140° with soda lime glass. A narrow tube of radius 1.00 mm made of this glass is dipped in a trough containing mercury. By what amount does the mercury dip down in the tube relative to the liquid surface outside? Surface tension of mercury at the temperature of the experiment is 0.465 N m–1. Density of mercury = 13.6 × 103 kg m–3
Define surface tension and surface energy.
It is said that a liquid rises or is depressed in capillary due to the surface tension. If a liquid neither rises nor depresses in a capillary, can we conclude that the surface tension of the liquid is zero?
A uniform vertical tube of circular cross section contains a liquid. The contact angle is 90°. Consider a diameter of the tube lying in the surface of the liquid. The surface to the right of this diameter pulls the surface on the left of it. What keeps the surface on the left in equilibrium?
Frictional force between solids operates even when they do not move with respect to each other. Do we have viscous force acting between two layers even if there is no relative motion?
A heavy mass is attached to a thin wire and is whirled in a vertical circle. The wire is most likely to break
If two soap bubbles of different radii are connected by a tube,
Water rises in a vertical capillary tube up to a length of 10 cm. If the tube is inclined at 45°, the length of water risen in the tube will be
A 20 cm long capillary tube is dipped in water. The water rises up to 8 cm. If the entire arrangement is put in a freely falling elevator, the length of water column in the capillary tube will be
The rise of a liquid in a capillary tube depends on
(a) the material
(b) the length
(c) the outer radius
(d) the inner radius of the tube
Consider a small surface area of 1 mm2 at the top of a mercury drop of radius 4.0 mm. Find the force exerted on this area (a) by the air above it (b) by the mercury below it and (c) by the mercury surface in contact with it. Atmospheric pressure = 1.0 × 105 Pa and surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1. Neglect the effect of gravity. Assume all numbers to be exact.
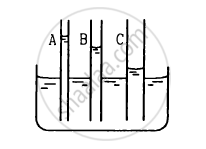
The capillaries shown in figure have inner radii 0.5 mm, 1.0 mm and 1.5 mm respectively. The liquid in the beaker is water. Find the heights of water level in the capillaries. The surface tension of water is 7.5 × 10−2 N m−1.
A barometer is constructed with its tube having radius 1.0 mm. Assume that the surface of mercury in the tube is spherical in shape. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to 76 cm of mercury, what will be the height raised in the barometer tube? The contact angle of mercury with glass = 135° and surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1. Density of mercury = 13600 kg m−3.
Two large glass plates are placed vertically and parallel to each other inside a tank of water with separation between the plates equal to 1 mm. Find the rise of water in the space between the plates. Surface tension of water = 0.075 Nm−1.
Find the force exerted by the water on a 2 m2 plane surface of a large stone placed at the bottom of a sea 500 m deep. Does the force depend on the orientation of the surface?
A cubical block of ice floating in water has to support a metal piece weighing 0.5 kg. Water can be the minimum edge of the block so that it does not sink in water? Specific gravity of ice = 0.9.
A cubical box is to be constructed with iron sheets 1 mm in thickness. What can be the minimum value of the external edge so that the cube does not sink in water? Density of iron = 8000 kg/m3 and density of water = 1000 kg/m3.
A cubical metal block of edge 12 cm floats in mercury with one fifth of the height inside the mercury. Water in it. Find the height of the water column to be poured.
Specific gravity of mercury = 13.6.
A solid sphere of radius 5 cm floats in water. If a maximum load of 0.1 kg can be put on it without wetting the load, find the specific gravity of the material of the sphere.
The energy stored in a soap bubble of diameter 6 cm and T = 0.04 N/m is nearly ______.
Derive an expression for capillary rise for a liquid having a concave meniscus.
Calculate the rise of water inside a clean glass capillary tube of radius 0.1 mm, when immersed in water of surface tension 7 × 10-2 N/m. The angle of contact between water and glass is zero, the density of water = 1000 kg/m3, g = 9.8 m/s2.
A drop of mercury of radius 0.2 cm is broken into 8 droplets of the same size. Find the work done if the surface tension of mercury is 435.5 dyn/cm.
The surface tension of a liquid at critical temperature is ______
What will be the shape of the liquid meniscus for the obtuse angle of contact?
How does the friction arise between the surfaces of two bodies in relative motion?
How does surface tension help a plant?
Define the angle of contact for a given pair of solid and liquid.
Obtain an expression for the surface tension of a liquid by the capillary rise method.
Two spherical rain drops reach the surface of the earth with terminal velocities having ratio 16 : 9. The ratio of their surface area is ______.
The excess of pressure, due to surface tension, on a spherical liquid drop of radius 'R' is proportional to ______.
A large number of liquid drops each of radius 'r' coalesce to form a big drop of radius 'R'. The energy released in the process in converted into kinetic energy of the big drop. The speed of the big drop is ______. (T = surface tension of liquid, p = density of liquid)
A molecule of water on the surface experiences a net ______.
The upward force of 105 dyne due to surface tension is balanced by the force due to the weight of the water column and 'h' is the height of water in the capillary. The inner circumference of the capillary is ______.
(surface tension of water = 7 × 10-2 N/m)
Soap solution is used for cleaning dirty clothes because ______.
The free surface of oil in a tanker, at rest, is horizontal. If the tanker starts accelerating the free surface will be titled by an angle θ. If the acceleration is a ms–2, what will be the slope of the free surface?
This model of the atmosphere works for relatively small distances. Identify the underlying assumption that limits the model.
Surface tension is exhibited by liquids due to force of attraction between molecules of the liquid. The surface tension decreases with increase in temperature and vanishes at boiling point. Given that the latent heat of vaporisation for water Lv = 540 k cal kg–1, the mechanical equivalent of heat J = 4.2 J cal–1, density of water ρw = 103 kg l–1, Avagadro’s No NA = 6.0 × 1026 k mole–1 and the molecular weight of water MA = 18 kg for 1 k mole.
- Estimate the energy required for one molecule of water to evaporate.
- Show that the inter–molecular distance for water is `d = [M_A/N_A xx 1/ρ_w]^(1/3)` and find its value.
- 1 g of water in the vapor state at 1 atm occupies 1601 cm3. Estimate the intermolecular distance at boiling point, in the vapour state.
- During vaporisation a molecule overcomes a force F, assumed constant, to go from an inter-molecular distance d to d ′. Estimate the value of F.
- Calculate F/d, which is a measure of the surface tension.
Two narrow bores of diameter 5.0 mm and 8.0 mm are joined together to form a U-shaped tube open at both ends. If this U-tube contains water, what is the difference in the level of the two limbs, of the tube?
[Take surface tension of water T = 7.3 × 10-2 Nm-1, angle of contact = 0, g = 10 ms-2 and density of water = 1.0 × 103 kgm-3]
A soap bubble of radius 3 cm is formed inside another soap bubble of radius 6 cm. The radius of an equivalent soap bubble which has the same excess pressure as inside the smaller bubble with respect to the atmospheric pressure is ______ cm.
When an air bubble of radius r rises from the bottom to the surface of a lake, its radius becomes `(5r)/4`. Taking the atmospheric pressure to be equal to the 10 m height of the water column, the depth of the lake would approximately be ______.
(ignore the surface tension and the effect of temperature)
The surface tension of a soap solution is T. The work done in blowing a soap bubble of diameter d to that of a diameter 2d is ______.
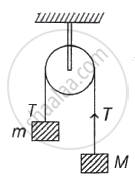
Two blocks of masses m and M are connected by means of a metal wire of cross-sectional area A passing over a frictionless fixed pully as shown in the figure. The system is then released. If M = 2m, then the stress produced in the wire is ______.
Find the work done when a drop of mercury of radius 2 mm breaks into 8 equal droplets. [Surface tension of mercury = 0.4855 J/m2].
