Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain aldol condensation reaction in detail.
Solution
- Aldehydes containing at least one α–hydrogen atom undergo a reaction in presence of dilute alkali (dilute NaOH, KOH, or Na2CO3) as the catalyst to form β-hydroxy aldehydes (aldol). This reaction is known as the aldol reaction.
- Formation of aldol is an addition reaction.
- Aldol formed from aldehyde having α-hydrogens undergoes subsequent elimination of water molecule on warming. This gives rise to α,β-unsaturated aldehyde.
- The overall reaction is called aldol condensation. It is a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction.
- The reaction can be given as,
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{\underset{\text{Aldehyde}}{2R - CH2 - CHO} ->[aq.NaOH] R - CH2 - CH - CHR - CHO}\\
\phantom{.......................}|\\
\phantom{..........................}\ce{\underset{\text{Aldol}}{OH}}
\end{array}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{R - CH2 - CH - CHR - CHO ->[-H2O][warm] \underset{\text{α,β-Unsaturated aldehyde}}{R - CH = CR - CHO}}\\
|\phantom{.......................................}\\
\ce{\underset{Aldol}{OH}}\phantom{.....................................}
\end{array}\]
e.g.
- Ketones containing at least two α-hydrogen also undergo aldol condensation reaction and give an α,β-unsaturated ketone.
e.g.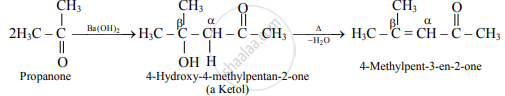
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Aldol
Which of the following compounds would undergo aldol condensation, which the Cannizzaro reaction and which neither? Write the structures of the expected products of aldol condensation and Cannizzaro reaction.
- Methanal
- 2-Methylpentanal
- Benzaldehyde
- Benzophenone
- Cyclohexanone
- 1-Phenylpropanone
- Phenylacetaldehyde
- Butan-1-ol
- 2, 2-Dimethylbutanal
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Benzaldehyde to 3-Phenylpropan-1-ol
Describe the following:
Cross aldol condensation
Give reasons Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect.
Why is alpha (α) hydrogen of carbonyl compounds acidic in nature?
Write chemical equations of the following reaction :
Propanone is treated with dilute Ba (OH)2-.
Write chemical equations of the following reaction :
Benzoyl chloride is hydrogenated in the presence of `"Pd"/(BaSO_4)`
Write a chemical equation for the following reaction:
Propanone is treated with dilute Ba( OH)2.
What is substituted imine called?
Cannizaro’s reaction is not given by ______.
Why is there a large difference in the boiling points of butanal and butan-1-ol?
Compound ‘A’ was prepared by oxidation of compound ‘B’ with alkaline \[\ce{KMnO4}\]. Compound ‘A’ on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride gets converted back to compound ‘B’. When compound ‘A’ is heated with compound B in the presence of \[\ce{H2SO4}\] it produces fruity smell of compound C to which family the compounds ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ belong to?
Why are carboxylic acids more acidic than alcohols or phenols although all of them have hydrogen atom attached to a oxygen atom \[\ce{(-O-H)}\]?
Assertion: The α-hydrogen atom in carbonyl compounds is less acidic.
Reason: The anion formed after the loss of α-hydrogen atom is resonance stabilised.
Give reasons to support the answer:
Presence of Alpha hydrogen in aldehydes and ketones is essential for aldol condensation.
Identify A and B from the following reaction:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}\\
|\phantom{....................}\\
\phantom{}\ce{2CH3 - C = O ->[Ba(OH)2] A ->[Δ] B + H2O}
\end{array}\]
Predict the reagent for carrying out the following transformations:
Ethanal to 3-hydroxy butanal
\[\ce{CH3-CH2-CHO ->[dil][alkali] Product}\]
The product in the above reaction is:
The major product of the following reaction is:
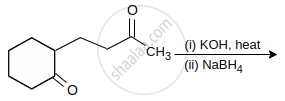
Which of the following does not give aldol condensation reaction?
Which of the following compounds will undergo self-condensation in the presence of dilute NaOH solution?

Identify A and B:
When acetaldehyde is treated with dilute NaOH, the following reaction is observed.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{2CH3 - CHO ->[dil.NaOH] CH3 - CH - CH2 - CHO}\\
\phantom{...............}|\\
\phantom{.................}\ce{OH}
\end{array}\]
- What are the functional groups in the product?
- Can another product be formed during the same reaction? (Deduce the answer by doing atomic audit of reactant and product).
- Is this an addition reaction or condensation reaction?
What is aldol condensation? Explain it with suitable examples.
