Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the phenomena of surface tension on the basis of molecular theory.
Solution
Molecular theory of surface tension:
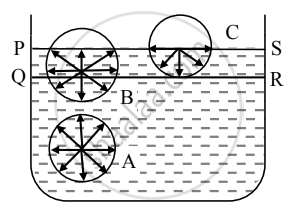
- Let PQRS = Surface film of liquid in a container containing liquid. PS is the free surface of the liquid and QR is the inner layer parallel to PS at distance equal to the range of molecular force.
- Now consider three molecules A, B, and C in a liquid in a vessel such that molecule A is well inside the liquid, molecule B within the surface film, and molecule C is on the surface of the liquid as shown in the figure.
- The sphere of influence of molecule A is entirely inside the liquid. As a result, molecule A is acted upon by equal cohesive forces in all directions. Thus, the net cohesive force acting on molecule A is zero.
- For molecule B, a large part of its sphere of influence is inside the liquid and a smaller part is outside the surface (in the air). The adhesive force acting on molecule B due to air molecules above it and within its sphere of influence is weak compared to the strong downward cohesive force acting on the molecule. As a result, molecule B gets attracted inside the liquid.
- For molecule C, half of the sphere of influence is in air and half is in liquid. As the density of air is much less than that of liquid, the number of air molecules within the sphere of influence of molecule C above the free surface of the liquid is much less than the numbers of liquid molecules within the sphere of influence that lies within the liquid. Thus, the adhesive force due to the air molecules acting on molecule C is weak compared to the cohesive force acting on the molecule. As a result, molecule C also gets attracted inside the liquid.
- Thus, all molecules in the surface film are acted upon by an unbalanced net cohesive force directed into the liquid. Therefore, the molecules in the surface film are pulled inside the liquid. This minimizes the total number of molecules in the surface film. As a result, the surface film remains under tension. The surface film of a liquid behaves like a stretched elastic membrane. This tension is known as surface tension and the force due to it acts tangential to the free surface of a liquid.
RELATED QUESTIONS
The energy of the free surface of a liquid drop is 5π times the surface tension of the liquid. Find the diameter of the drop in C.G.S. system.
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing forces acting on the meniscus of water in a capillary tube.
'n' droplets of equal size of radius r coalesce to form a bigger drop of radius R. The energy liberated is equal to...................
(T =Surface tension of water)
`(a) 4piR^2T[n^(1/3)-1]`
`(b) 4pir^2T[n^(1/3)-1]`
`(c) 4piR^2T[n^(2/3)-1]`
`(d)4 pir^2T[n^(2/3)-1]`
The surface tension of water at 0ºc is 75·5 dyne/cm. Find surface tension of water at 25°C. [ α for water = 0·0021/°C ]
Explain why Surface tension of a liquid is independent of the area of the surface
A U-shaped wire is dipped in a soap solution and removed. The thin soap film formed between the wire and the light slider supports a weight of 1.5 × 10–2 N (which includes the small weight of the slider). The length of the slider is 30 cm. What is the surface tension of the film?
What is the excess pressure inside a bubble of soap solution of radius 5.00 mm, given that the surface tension of soap solution at the temperature (20 °C) is 2.50 × 10–2 N m–1? If an air bubble of the same dimension were formed at depth of 40.0 cm inside a container containing the soap solution (of relative density 1.20), what would be the pressure inside the bubble? (1 atmospheric pressure is 1.01 × 105 Pa).
Mercury has an angle of contact equal to 140° with soda lime glass. A narrow tube of radius 1.00 mm made of this glass is dipped in a trough containing mercury. By what amount does the mercury dip down in the tube relative to the liquid surface outside? Surface tension of mercury at the temperature of the experiment is 0.465 N m–1. Density of mercury = 13.6 × 103 kg m–3
Two narrow bores of diameters 3.0 mm and 6.0 mm are joined together to form a U-tube open at both ends. If the U-tube contains water, what is the difference in its levels in the two limbs of the tube? Surface tension of water at the temperature of the experiment is 7.3 × 10–2 N m–1. Take the angle of contact to be zero and density of water to be 1.0 × 103 kg m–3 (g = 9.8 m s–2)
Define surface tension and surface energy.
Show that the surface tension of a liquid is numerically equal to the surface energy per unit
area.
When a glass capillary tube is dipped at one end in water, water rises in the tube. The gravitational potential energy is thus increased. Is it a violation of conservation of energy?
If a mosquito is dipped into water and released, it is not able to fly till it is dry again. Explain
Water near the bed of a deep river is quiet while that near the surface flows. Give reasons.
If water in one flask and castor oil in other are violently shaken and kept on a table, which will come to rest earlier?
A heavy mass is attached to a thin wire and is whirled in a vertical circle. The wire is most likely to break
Air is pushed into a soap bubble of radius r to double its radius. If the surface tension of the soap solution in S, the work done in the process is
The excess pressure inside a soap bubble is twice the excess pressure inside a second soap bubble. The volume of the first bubble is n times the volume of the second where n is
The properties of a surface are different from those of the bulk liquid because the surface molecules
(a) are smaller than other molecules
(b) acquire charge due to collision from air molecules
(c) find different type of molecules in their range of influence
(d) feel a net force in one direction.
A liquid is contained in a vertical tube of semicircular cross section. The contact angle is zero. The force of surface tension on the curved part and on the flat part are in ratio
When a capillary tube is dipped into a liquid, the liquid neither rises nor falls in the capillary.
(a) The surface tension of the liquid must be zero.
(b) The contact angle must be 90°.
(c) The surface tension may be zero.
(d) The contact angle may be 90°.
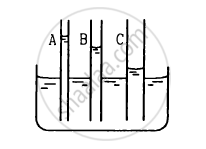
The capillaries shown in figure have inner radii 0.5 mm, 1.0 mm and 1.5 mm respectively. The liquid in the beaker is water. Find the heights of water level in the capillaries. The surface tension of water is 7.5 × 10−2 N m−1.
The lower end of a capillary tube is immersed in mercury. The level of mercury in the tube is found to be 2 cm below the outer level. If the same tube is immersed in water, up to what height will the water rise in the capillary?
A capillary tube of radius 0.50 mm is dipped vertically in a pot of water. Find the difference between the pressure of the water in the tube 5.0 cm below the surface and the atmospheric pressure. Surface tension of water = 0.075 N m−1.
The lower end of a capillary tube of radius 1 mm is dipped vertically into mercury. (a) Find the depression of mercury column in the capillary. (b) If the length dipped inside is half the answer of part (a), find the angle made by the mercury surface at the end of the capillary with the vertical. Surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1 and the contact angle of mercury with glass −135 °.
Find the force exerted by the water on a 2 m2 plane surface of a large stone placed at the bottom of a sea 500 m deep. Does the force depend on the orientation of the surface?
A metal piece of mass 160 g lies in equilibrium inside a glass of water. The piece touches the bottom of the glass at a small number of points. If the density of the metal is 8000 kg/m3, find the normal force exerted by the bottom of the glass on the metal piece.

A ferry boat has internal volume 1 m3 and weight 50 kg.(a) Neglecting the thickness of the wood, find the fraction of the volume of the boat immersed in water.(b) If a leak develops in the bottom and water starts coming in, what fraction of the boat's volume will be filled with water before water starts coming in from the sides?
A cube of ice floats partly in water and partly in K.oil (in the following figure). Find the ratio of the volume of ice immersed in water to that in K.oil. Specific gravity of K.oil is 0.8 and that of ice is 0.9.

A cubical metal block of edge 12 cm floats in mercury with one fifth of the height inside the mercury. Water in it. Find the height of the water column to be poured.
Specific gravity of mercury = 13.6.
A solid sphere of radius 5 cm floats in water. If a maximum load of 0.1 kg can be put on it without wetting the load, find the specific gravity of the material of the sphere.
The energy stored in a soap bubble of diameter 6 cm and T = 0.04 N/m is nearly ______.
Why is the surface tension of paints and lubricating oils kept low?
How much amount of work is done in forming a soap bubble of radius r?
Explain the capillary action.
The water droplets are spherical in free fall due to ______
Water rises to a height of 20 mm in a capillary tube. If the radius made 1/3rd of its previous value, to what height will the water now rise in the tube?
Obtain an expression for the capillary rise or fall using the forces method.
How does the friction arise between the surfaces of two bodies in relative motion?
The wettability of a surface by a liquid depends primarily on
Define the angle of contact for a given pair of solid and liquid.
A drop of oil placed on the surface of water spreads out. But a drop of water place on oil contracts to a spherical shape. Why?
Obtain an expression for the surface tension of a liquid by the capillary rise method.
Water rises in a capillary tube of radius r upto a height h. The mass of water in a capillary is m. The mass of water that will rise in a capillary of radius `"r"/4` will be ______.
The upward force of 105 dyne due to surface tension is balanced by the force due to the weight of the water column and 'h' is the height of water in the capillary. The inner circumference of the capillary is ______.
(surface tension of water = 7 × 10-2 N/m)
Eight droplets of water each of radius 0.2 mm coalesce into a single drop. Find the decrease in the surface area.
A drop of water and a soap bubble have the same radii. Surface tension of soap solution is half of that of water. The ratio of excess pressure inside the drop and bubble is ______.
In a U-tube, the radii of two columns are respectively r1 and r2. When a liquid of density ρ(θ = 0°) is filled in it, a level difference of h is observed on two arms, then the surface tension of the liquid is ______.
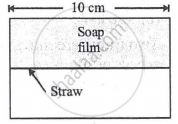
A soap film of surface tension 3 × 10-2 formed in a rectangular frame can support a straw as shown in Fig. If g = 10 ms-12, the mass of the straw is ______.
Calculate (i) the pressure due to the weight of the water at a depth of 2.5 m and (ii) the depth below the surface of water at which the pressure due to the weight of the water equals 1.0 atm.
The surface tension of boiling water is ______.
